Rise of the Connector as Modern Day Digital Influencer
Connectors are making inroads into every corner of our lives as digital influencers.

We exist in a connected world of products, services, communication tools, and transportation networks that are designed to increase our standard of living, make us smarter, and bring us closer to the people and places we care about.
Fundamental to this is electronics, which have evolved over the past four decades per Moore’s Law, an observation that the number of transistors inside of chips will expand two-fold every two years. As a result, transistors are packaged far more densely than ever and breakthrough nano-scale devices are now assembled on multi-layer circuit boards.
Beyond the chip, other components play critical roles as well. What if boards weren’t tethered by wires? A car’s audio system, for instance, won’t function if PCB-wire bonding is broken due to shock, strain, or vibration. Connectors, however, add durability and reliability. In a smart watch, connectors sewn into tiny boards enable it to provide reliable heart rate readings, for example, and connect to the Internet of Things (IoT), the connected technology that makes cities smarter, vehicles safer, and factories autonomous.
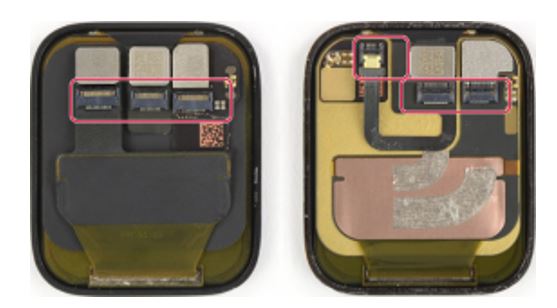
Miniature connectors inside a smart watch (Courtesy: ifixit)
Connectors are making inroads into the furthermost corners of our lives as digital influencers.
5G, IoT, and data center
5G, the fifth generation mobile technology standard, caters to smart phones and also to a vast collection of nodes and sensors in devices used in the commercial, transportation, and medical sectors. These IoT devices are deployed with specific IP addresses and constantly communicate with each other using low amounts of power. Numerous traffic channels are simultaneously processed and routed through 5G antennas, baseband units, long haul fiber optic cabling, and edge-based data centers. Bandwidth must be adequate to prevent latency, as lags in data transfer would negatively impact performance across the network.
All this cloud-based connectivity depends on data centers. Initially, data centers were complex and centrally located. Modern data centers are decentralized and compact, providing greater computing power with a lower carbon footprint and reduced user costs. Hyperscale virtual computing based on commercial off-the-shelf servers replicates the nuances of compute, storage, and networking handled by dedicated hardware like SAN, NAS, routers, or switches. This promotes the scalability, modularity, and simplicity required for edge colocation deployments. Open standards from consortia like the OCP and ODCC optimize power distribution to promote energy efficiency and minimalize environmental impact.
Smart cities and buildings
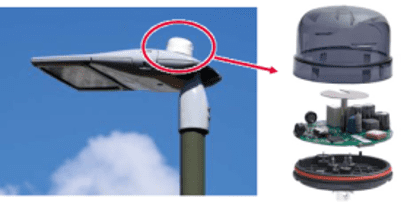
With 5G and IoT, smart cities are now even smarter. Sensors and cameras installed on poles, traffic signals, billboards, rooftops, building walls, and underground use ultra-low power protocols like LoRaWAN, where they monitor and manage public assets related to lighting, environment, weather, traffic, and parking, as well as metering and monitoring air, gas, water, or energy. Individual buildings are becoming greener through automated HVAC, lighting, and energy metering. These systems use AI to remotely process data rather than waiting to hand it over to the central cloud, creating instantaneous communications that help critical entities like disaster management respond on time. Early warning systems that alert motorists that pedestrians are present, streetlamps with information displays, driverless taxis, hassle-free public transportation, and protection of civilian identity are a few examples of how machine-to-machine communication enriches life in smart cities.
For the consumer
Consumer electronics are smarter than ever. Content streams across HDTVs, game consoles, and virtual reality headsets. Powerful software and HD cameras on smartphones, tablets, and notebooks can make anyone a creative artist. Even our clothing, watches, wallets, and glasses can have smart capabilities.
Smart technology adds safety and convenience to homes. Garages and doors detect homeowners and let them in. Thermostats, lights, and blinds adjust to environmental conditions and individual tastes. Smart speakers respond to commands and remotely operate appliances, entertainment systems, and smart meters. Sensors, plugs, and switches with AI detect fire or burglary. Smart meters inform utilities of power consumed from the grid or fed back from shingled solar panels. Smart homes are here.
Autonomous and e-mobility solutions improve personal transportation. Cameras, lidar, UV, and ADAS steer cars through lanes, obstacles, and traffic. Charging stations provide fast and wireless EV charging. Light-commute e-bikes with pedal-assist and on-board computers are joining bicycle sharing programs.
Industry and Energy 4.0
Process-controlled factory automation in the food and beverage, automobile, and material and goods industry involves industrial PCs and programmable logic controllers (PLC) working servo drives, motors, valves, and actuators using protocols like industrial Ethernet, TCP/IP, Modbus, and Profibus. Now, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Industry 4.0 can empower AI to accomplish tasks such as:
- Read and control each traditional PLC, Ethernet switch, PC, or gateway from any corner of the world through a mobile device or a smart speaker.
- Equip robotic arms to go collaborative and fenceless through dynamic trajectory adjustments to promote worker safety and save installation costs.
- Bring Ethernet connectivity to each smart sensor or actuator to form an IIoT system and channel their diagnostic data to the cloud for live tracking and predictive maintenance.
- Perform failure traceability to detect faults and order replacements for worn-out parts.
The renewable energy sector follows industry closely. Wind turbines and solar farms supply fluctuating AC/DC power to intelligent conversion systems and large reservoir batteries before feeding metered energy to the smart grid. Numerous intelligent electronic devices (IED) in the grid monitor voltage, phase, current, and frequency of transformers and circuit breakers and feed diagnostic data through Ethernet gateways to the cloud. Big data and AI bring efficiency and reduce carbon emissions by effectively managing all aspects from generation to storage, and from transmission to distribution.
Role of connectors
Interconnect manufacturers work closely with equipment manufacturers and component suppliers to propose, develop, and test innovative prototypes and solutions that favor commercial rollout. High-speed data, high-power transmission, and space-savings are priorities, with an emphasis on how electromagnetic susceptibility, thermodynamics, and air flow affect contact pins, board traces, wires, and housing. Cost-to-performance ratio is tested with varying compositions of precious-metal-alloy plating. Recent advancements in interconnects like PCIe 6.0 and DDR5 have mirrored developments in peripheral and memory technologies. Encoding schemes like PAM4, and electro-magnetically compliant signaling rates as high as 50 GHz, have influenced form factors and interfaces like the QSFP-DD and MPO 32 Fiber. High-performance computing has influenced performance-oriented architectures like orthogonal midplane, overpass cabling, and cabled backplane systems.
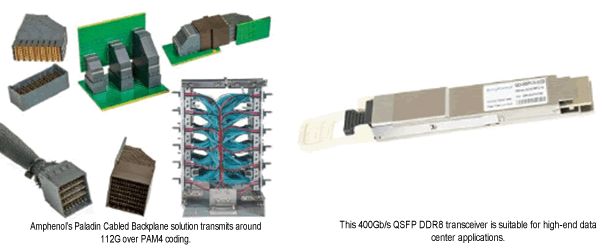
Amphenol Communication Solutions’ Paladin 112Gb/s Backplane Connector and 400 Gb/s DDR8 transceiver
Some connector suppliers even double as system integrators of data center racks and switching cabinets by choosing the type of fiber, transceiver, cable length, or multiplexing scheme that can be scaled up to 400 Gb/s of bandwidth if the customer prefers a high-end solution.
Looking inside each sensor, driver, controller, meter, camera, plug, switch, or thermostat that mobilizes smart cities, buildings, and smart homes, we see connectors placed on or near motherboards, power supplies, batteries, keypads, radios, speakers, or motors. Some are input-output types like the USB or HDMI, some are board-to-board and wire-to-board, some are lighting socket compliant drivers based on Zhaga, and some are protected against harsh environments, water, and dust ingress.
Application diversity is required because not all connectors can withstand shock and vibration inside cars. They must pass USCAR2 tests and sport error-proof, mis-mating and floating tolerant designs. Some must meet ADAS-friendly protocols like gigabit Ethernet. For e-bikes, connectors sourcing power from battery to motor must have waterproof sealing.
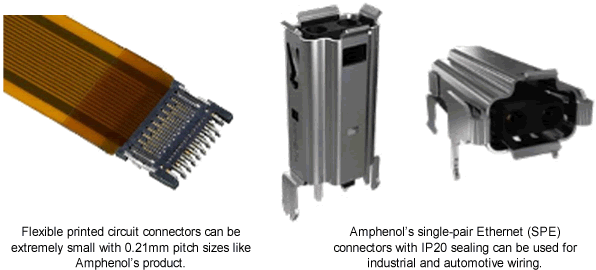
As technology influences connector development, so connectors influence technology. Their simplicity has inspired developments on both a holistic and revolutionary level. They are vanguards of refinement, precision, durability, and reliability on which novel designs are conceived.
Visit Amphenol Communications Systems online to learn more about influential connector products.
References
Garms, et al., “Capturing value at scale in discrete manufacturing with Industry 4.0,” McKinsey& Company.
Fritsche, et al., “Single-pair Ethernet: The Infrastructure for IIoT,” Automation 2021: IIoT & Industry 4.0 – Fueling Post-Pandemic Prosperity.
Russell, “Bringing Your Factory to the Edge in 2021,” Automation 2021: IIoT & Industry 4.0 – Fueling Post-Pandemic Prosperity.
Chokkattu, “Lyft’s Revamped Bike-Share Ebike Is Sleek—and Beefy.” Wired.
Teba, “ENERGY 4.0: How digital revolution is shaping the future of electricity.” Dexma.
Varghese, “Why Are Automotive OEMs Asking For Multi-Gig Automotive Ethernet.” Keysight.
Moel, “The Fallacy of Fencelessness and Why Cage Free is Best.” Veo Robotics.
Silverstein, “Solar-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Are Just Around the Corner.” Forbes.
Critchley, “Where Nanotechnology, the IoT, and Industry 4.0 Meet.” Mouser.
“3nm Technology.” TSMC.
“400G Takes Ethernet into a New Era.” Accton.
“Desigo System.” Siemens.
“Everything You Need to Know About Smart Home Technology.” Otelco.
“Heralding the Pcb Possibilities Of Tomorrow.” Nano Di.
“Nanoelectronics – Nanotechnology in Electronics.” Nanowerk.
Like this article? Check out our other New Technology, Data Centers, and Connector Industry News features and our 2022 and 2021 Article Archives.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- Rise of the Connector as Modern Day Digital Influencer - January 25, 2022