What are Backplane Connectors?
Meet the Connector: Backplane Connectors
Backplane connectors, or simply backplanes, are a type of board-to-board connector. The name backplane comes from their early use in mainframe computers because they were located against the back of the computer case. Today backplane connectors are generally used in top-of-rack switch applications or hybrid hard drive (HHD) clusters.
Expansion slots or sockets in the backplane are used to connect printed circuit boards (PCBs). In addition to connecting PCBs, backplanes integrate other system components, known as daughterboards. Parallel backplane connectors form a complete computer bus, which supports several daughterboards.
Backplane connectors are popular and widely used in the design of custom computer systems due to their versatility, scalability, modularity, and ease of use. They are considered more dependable than cables, which are subject to continual flexing that causes them to wear out more quickly.
Typically, backplanes do not have microprocessors, CPUs, chipsets, cache, or other active components. However, a backplane can function as a motherboard when connected to a single board computer or a system host board. This type of backplane is called active.
Passive backplanes have bus connectors. In some applications, they have buses (to transmit data from one part of a computer to another) and drivers (to interface hardware devices to an operating system).
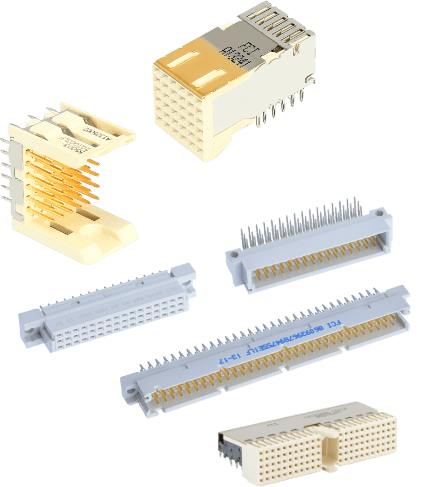
The Amphenol FCI industrial backplane connector range is one of the broadest and includes hard metric connectors, future bus connectors, and DIN 41612 connectors. Performing to industry standards such as IEC, Compact PCI, and EN44545, these robust, feature-packed, compact connectors are designed for use in rugged applications in Industrial, Instrumentation, Smart Grid, Wind Energy, Communications, Medical, Railways, and Avionics.
Design Notes for Backplane Connectors
Standards
- ARINC 659 defines the electrical characteristics for a controlled impedance backplane bus for use with Integrated Modular Avionics (IMA).
- DIS-MISC-81063 is a backplane component implementation plan.
- EIA-616 applies to modular two-part connectors for printed wiring boards in equipment for telecommunication or electronic devices using similar techniques.
Form Factors. Industrial backplanes support AT, ATX, terminal block, or 3.3 V power connectors. Form factors include:
- Advanced technology (AT)
- Low profile (LPX)
- ATX (miniATX and microATX)
- NLX
- Size A (100 mm x 160 mm), Size B (233 x 160 mm), Size C (233 x 340 mm), and Size D cards (360 mm x 340 mm)
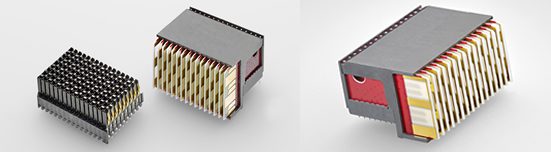
TE Connectivity’s (TE) MULTIGIG RT 2-S (left) and MULTIGIG RT 3 next generation lightweight, rugged, high speed backplane connectors meet the interface dimensions for VITA 46 VPX connectors. They are backward compatible with legacy MULTIGIG RT products and offer the same reliable interface. The new contact and wafer designs optimize signal integrity, extending data rates from 16-32+ GB/s.
Bus Types. Backplanes use different buses, depending on the application. Some commonly used bus types are:
- Industry standard architecture (ISA) buses
- Peripheral component interconnect (PCI)
- Compact PCI (cPCI) in a Versa Module Eurocard (VME) bus
- The VME bus (VMEbus)
- VME extensions for instrumentation (VXI)
- Multisystem extension interface (MXI)
- Embedded technology extended (ETX)
- Embedded PCI extended (ePCI-X)
How to Specify Backplane Connectors
- How many segments in the card and expansion slots are needed? (Bus type determines the need for ISA, PCI, cPCI, PXI, VME, VXI, or MXI slots.)
- Does the backplane include a connector for a keyboard?
- Are there on-board terminators?
Markets and Applications for Backplane Connectors
Markets include industrial, commercial, military, space, medical, and telecom. Applications include computer servers, data storage systems, disc arrays and disc enclosures for power disc drives, telecom infrastructures, instrumentation, smart grid, wind energy, railways, and avionics.
Suppliers
Amphenol Aerospace, Amphenol Communications Solutions, HARTING, ept, Nicomatic, Powell Electronics, Samtec, Smiths Interconnect, SV Microwave, TE Connectivity
Related Products
Like this article? Check out our other Meet the Connector and Board-to-Board articles, our Datacom Market Page, and our 2022 and 2023 Article Archives.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- Sealing Success: Overmolding for More Secure Connections - April 23, 2024
- Medical Cable Assemblies Product Roundup - April 23, 2024
- Mezzanine Connectors Product Roundup - April 16, 2024







