What are Board-to-Board Connectors?
Meet the Connector: Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board (BTB) connectors are used to transmit signals between printed circuit boards (PCBs). They are made by many connector manufacturers and come in a variety of styles and materials. BTB connectors are among the commonly used connector types. Their evolution has been influenced by their use in an ever-growing number of consumer devices, and in connected devices in general, as the IoT and IIoT explode in use across industries.
A BTB connector consists of housing and terminals made of a conductive material, usually copper alloy. The terminals are plated for better conductivity and to protect against rust. BTB connectors can be mounted on the PCB with through-hole technology, in which pins are inserted through holes drilled in the board and soldered on the other side, or mounted directly onto the board, known as surface-mount technology (SMT).
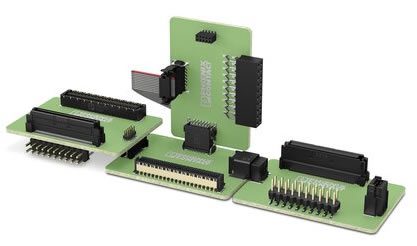
Phoenix Contact’s FINEPITCH series board-to-board connectors provides shielded and unshielded solutions for signal and data transmission. Individual PCB orientations in all dimensions with different designs, stack heights, and numbers of positions in different pitches from 0.635 mm to 2.54 mm are possible, as well as mezzanine, coplanar connections, and mother-daughter cards.
Types of Board-to-Board Connectors
Parallel backplane connectors form a complete computer bus, which supports several daughter boards. Backplanes, so named because in the days of mainframe computers they were located against the back of the computer case, are generally used in top-of-rack switch applications or HHD (hybrid hard drive) clusters.
Mezzanine connectors are high-speed, board-to-board connectors that connect two parallel PCBs in a stacking configuration.
Edge card connectors connect perpendicular to the motherboard in a coplanar configuration (on the same plane connected by two right-angle connectors.)
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) are used in small devices, such as consumer electronics, where small pin spacing makes larger versions impractical. FPCs often have a small pin pitch spacing, a low profile height, and can feature high-density arrangements. They can carry 80 pins with the smallest pin pitch at .25 mm (compared to a standard pin pitch of 1.25 mm.)
A floating connector absorbs misalignments in “x” and “y” directions that can occur when the interface is mounted on a PCB.

JAE’s AX01 series features a floating tolerance of +/-0.5 mm in both X & Y directions.
Design Notes
How to Specify: BTB connectors are specified by housing size and material, number of contacts, stacking height (measured from the circuit board), length of the contacts, number of contact rows, pin pitch, and termination method.
Signal integrity (SI) is the main consideration in choosing a BTB connector. The connector is critical to ensuring effective communication as the signal moves from the transmitter to the receiver, without distortion or disruption caused by crosstalk, return loss, attenuation, and EMI (electromagnetic interference).
Density refers to how closely the contacts are spaced. The closer the spacing, the more connections can be made in a particular area. BTB connectors with high density can reduce the weight and size of a connector.
Stack height determines the amount of space between parallel boards. The lower the stack height, the less space taken up by the connector.

Greenconn‘s floating board-to-board connectors allow for various PCB stacking heights. The spring-like floating mechanism within these connectors offers reliable and flexible solutions for industrial automation.
Markets, Sectors, and Applications
BTB connectors are used in Automotive, Consumer Electronics, Datacom, Industrial, Medical, Military/Aerospace, and Transportation markets.
Applications include medical devices, computer equipment, servers, communication equipment, instrumentation, and consumer devices.
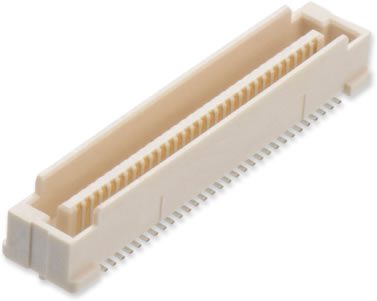
Harwin offers a range of board-to-board surface mount connectors for parallel board connection with a low stacking height. Tape and reeled for volume automation, high pin counts available.
Suppliers
Amphenol (TTI Inc.), Amphenol Communications Solutions, Greenconn, Hirose Electric, I-PEX, JAE, Molex, Norcomp, Phoenix Contact, Samtec, TE Connectivity, EX-EL Group, Harwin
Related products:
- Backplane connectors
- Mezzanine connectors
- Edge card connectors
Like this article? Check out our other Meet the Connector, board-to-board connectors, card edge connectors, and our Industrial Industry Page, and our 2022 Article Archive.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- State of the Industry: 2022-2023 Connector Sales - April 16, 2024
- Amphenol is On a Roll - April 2, 2024
- Nicomatic Proves That Two Heads are Better Than One - March 26, 2024





