Four Key Technology Trends Affecting Medical Device and Connector Manufacturers
Medical device manufacturers depend on innovative connectivity products to keep ahead of changes to the regulatory environment, as well as ongoing demand for low-cost, disposable solutions, reusable medical devices, and high-resolution imaging products.
While the quality and reliability of electronic equipment is vital for every industry, it is most critical in the medical industry, where human life and safety depend on equipment operating as intended. This formidable responsibility not only impacts medical device manufacturers, but the suppliers of every enabling component.
In order to help optimize patient outcomes, medical device manufacturers engage in research and development to develop innovative devices and add new electronic features to existing ones. In order to succeed, device manufacturers rely heavily on their connector manufacturers to continually push the envelope and deliver solutions that will effectively drive their most innovative product designs while also meeting size, cost, performance, and compliance demands. To support their manufacturing partners, connector suppliers draw upon their experience in other areas of the diverse medical device industry, as well as in other connector-critical market sectors — including the aviation, aerospace, and automotive industries — to overcome challenges. Current medical market trends driving collaboration between medical device and connector manufacturers include increased demand for safety and regulatory compliance, lower-cost disposable solutions, higher-resolution imaging capabilities, and enhanced durability.
Improved Safety and Regulatory Compliance
As medical devices continue to integrate additional features and functional capabilities, they grow more susceptible to effects of electrostatic discharge (ESD). Although static shocks are a widespread phenomenon, they can be hazardous in medical environments — causing software to freeze, reboot, or malfunction, damaging delicate circuity, or even shocking patients and operators. As a result, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) nearly doubled its ESD performance requirements in the fourth edition of the IEC 60601-1-2:2014 standard, which was published in 2014 and required global device compliance for new designs beginning December 31, 2018. The minimum voltage that a panel-mounted receptacle must withstand is now 15kV, measured from the receptacle housing to the internal electrical contacts, which represents a dramatic increase from the 8kV minimum mandated by the previous edition of the standard.
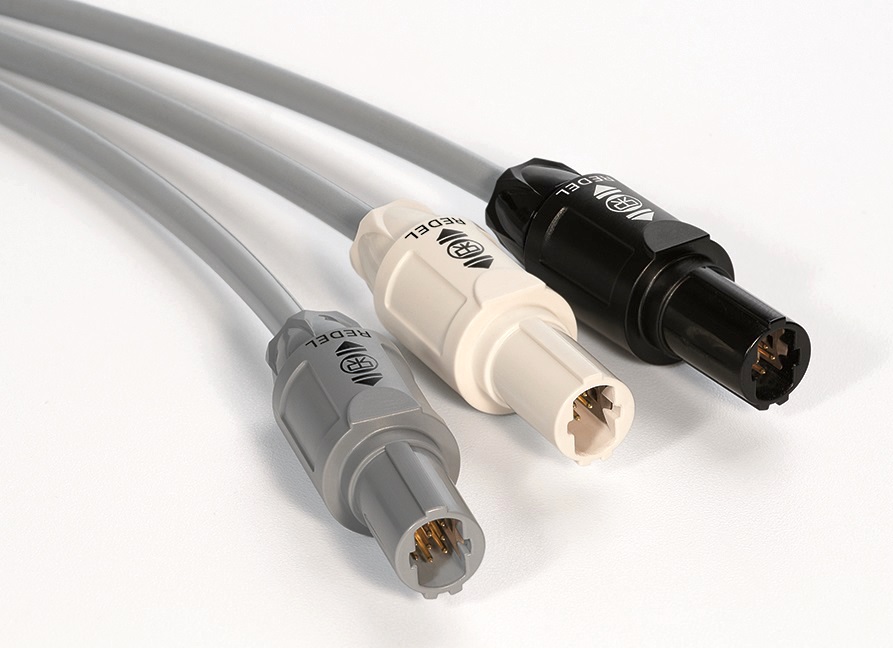

LEMO REDEL SP connectors feature eight additional high-density electrical contacts in the same small form factor and a tested ESD resistance of 25kV, which not only meets the new IEC standard but provides medical device designers plenty of room for future-proofing designs.
The IEC 60601 ESD standard provides an impetus for device manufacturers to reconsider longstanding equipment designs and proactively build in new capabilities, above and beyond those currently required by the standard. For example, some manufacturers are improving the safety, regulatory compliance compatibility, and functional capability of device designs by specifying touch-proof hybrid connectors with higher pin counts that offer additional benefits, including better sensors and imaging capabilities, and surpass the new 15kV ESD requirement. Touch-proof connectors enshroud all of the metal components within a plastic housing so there’s no chance of inadvertent contact with patients, doctors, or other personnel. They incorporate 360° internal metallic shielding to protect devices against electromagnetic and radio-frequency interference (EMI) in noisy environments, which can be a valuable upgrade in medical applications with high signal integrity requirements.
Lower-Cost Disposable Solutions
Coupled with the longstanding desire for lower-cost medical solutions is an increasing trend toward disposable devices. Medical device manufacturers are constantly imbuing their products with new and better capabilities to keep pace with market demands and remain competitive in a densely populated marketplace, so the significant cost constraints levied against disposable components present a real engineering challenge, especially since these devices still require advanced performance capabilities despite the fact that will only be used for one procedure and then thrown away. For example, the demand for higher-resolution imaging and mapping capabilities requires higher-density electrical contacts, but imaging equipment is one of the many medical device segments increasingly employing disposable devices. So, connector manufacturers must come up with creative solutions for minimizing cost while simultaneously enhancing capabilities.
Minimizing cost is an even greater concern in disposable medical applications. From the connector manufacturers’ point of view, the properties that can’t be compromised — like operating performance and reliability — must remain unchanged, while all those that can — like longevity — must be analyzed for potential cost-saving opportunities. Strategies include using high-quality but lower-cost materials that might be less mechanically or chemically robust than those employed in connectors designed to withstand thousands of steam cycles. High-cost materials still required by specific applications might be minimized, such as reducing gold-plating thicknesses in a redesigned component. Simplifying manufacturing procedures is another tactic and can include designing products in fewer parts, thereby utilizing fewer molds and simplifying assembly, or making greater use of automated assembly processes.
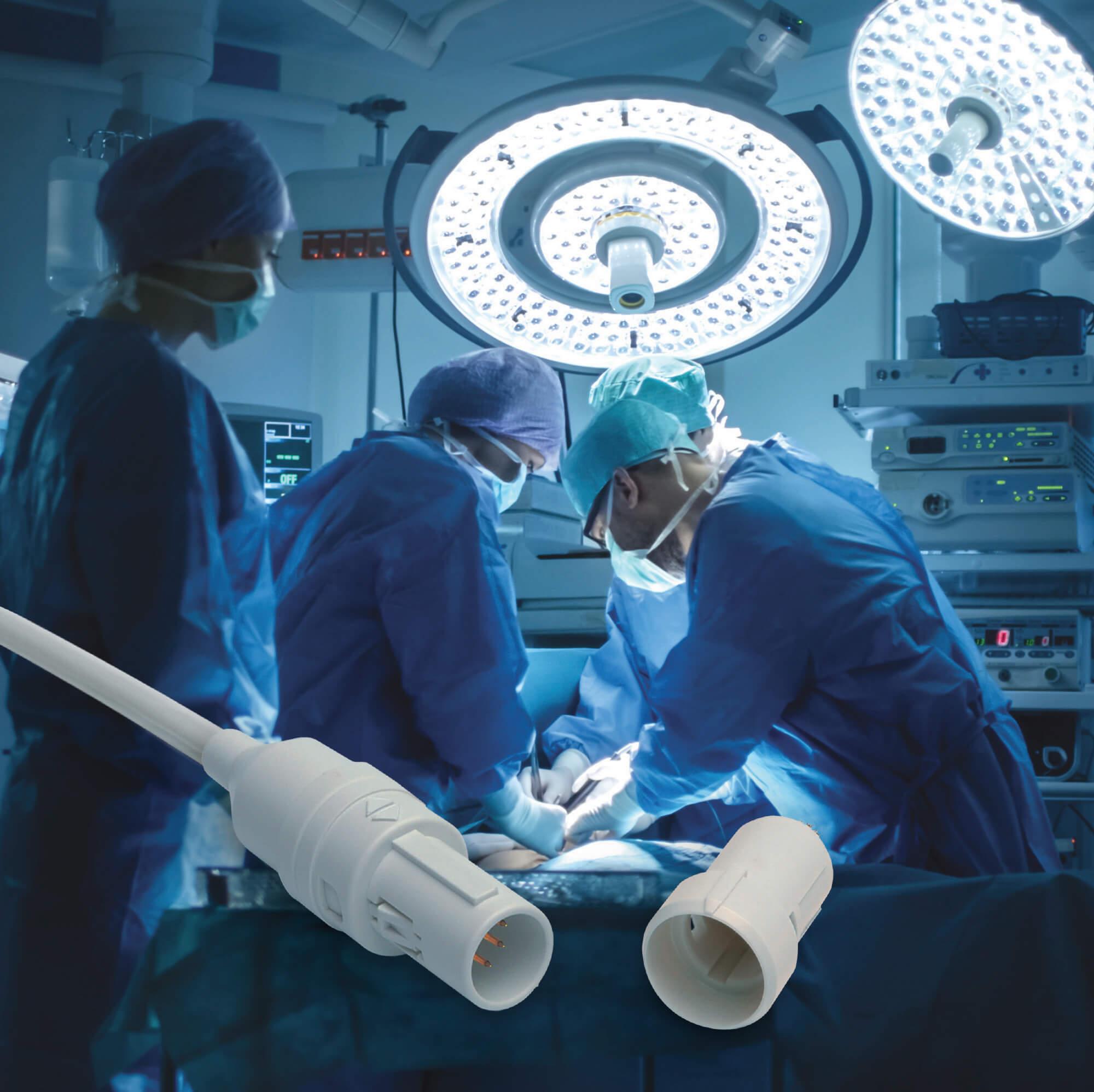
LEMO REDEL Single-Patient-Use Connectors for disposable medical applications like electrosurgical devices minimize content to economically justify a single use while retaining critical quality attributes of the reusable, sterilizable REDEL medical connectors they’re made to mate with, such as high-reliability gold-plated contacts.
Higher-Resolution Imaging Capabilities
In addition to driving a portion of the demand for disposable devices, the widespread demand for higher-resolution medical imaging capabilities is leading many medical device manufacturers to incorporate fiber optic connectivity technologies. Connector manufacturers with demonstrated expertise in developing advanced fiber optic contacts for use in telecommunications and industrial applications, where they’re more widely employed at present, can apply their knowledge to medical industry innovations as well. Fiber optic technology is safe and effective for transmitting high-speed, high-bandwidth data, like high-frequency imaging signals. However, the challenge lies in training end-users to clean the fibers regularly and properly to ensure optimal performance, so its employment is still spotty.
Enhanced Durability
Manufacturers are continually looking for better ways to protect the integrity of higher-end devices against the potential ravages of medical hazards, including multiple autoclave sterilization cycles, to lessen the cost per use or per lifetime. One of the most effective approaches is to enhance the durability of the device and its enabling components. To this end, connector manufacturers can utilize welded glass-to-metal or ceramic-to-metal hermetic vacuum seals, which have long been used in other critical industries, including the aerospace and oil and gas industries, and are proven to provide a superior degree of sealing integrity. The glass used in these applications is processed and fused at high temperatures around the metal, which effectively makes it break-resistant and prevents the leakage or ingress of liquid or gas of any kind. Hermetic seals are tested based on how many helium atoms can pass through at a certain leakage rate and are thus vastly superior to O-ring, epoxy, and other traditional sealing technologies. They can also be accomplished using a broad range of glass, metal, and/or ceramic materials to achieve an array of different combinations with various mechanical and insulating properties and costs.