Top Questions to Ask When Selecting Cable for Harsh Environment Applications
Failure-proof cable selection is especially important in dangerous or harsh environments where water, sunlight, temperature extremes, chemicals, dust, or other hazards are present.

Failure-proof cable selection starts with an evaluation of how the cable will be used and the environmental conditions that surround the application. This is especially important in dangerous or harsh environments where water, sunlight, temperature extremes, chemicals, dust, or other hazards are present.
Constant motion or twisting can cause internal conductor bundles to corkscrew, which can result in conductors breaking. Constant motion or flexing can create internal heat and abrasion, which may cause inner conductor insulation to fail and then short circuit. Other environmental factors, such as the presence of oil or chemicals, combined with constant motion, can accelerate failure of the cable’s outer jacket. Jacket failure in harsh environments that produce high heat or abrasion expose the inner conductors to the elements.
To prevent failure, ask (and answer) the right questions!
For failure-proof cable, gather the necessary information about how and where the cables will be used. Start with the basics:
- What are the specifications?
- What is the application environment? (What temperatures will the system operate in? If motion and flex are likely, will they be constant? Will the cable be exposed to oil, chemicals, UV rays, or welding slag, and if so, for how long?)
- How will the cable be installed, connectorized, and terminated?
- What agency standards, government regulations, and other approvals are needed?
- Are there aesthetic requirements for the finished cable assembly’s look and feel?
- What are the scheduling and budget parameters?
Once the overall details of the application have been established, determine the requirements for each cable component: strength member, breather tubes, water-blocking materials, fillers, barriers, shielding, and jackets.
Ruggedized Cable Components
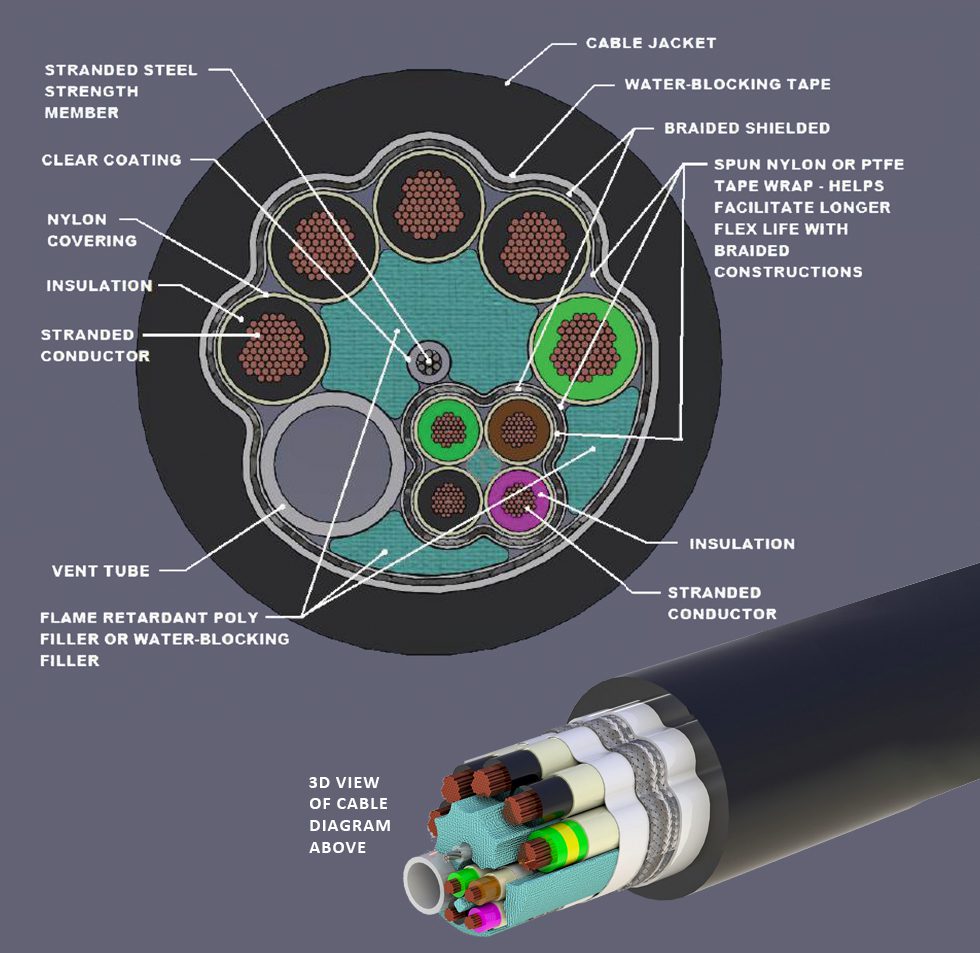
Strength member performance
Strengthening materials are added to improve pull strength, push strength, mechanical strength, or rigidity. Common strength members are fiberglass rods, steel, and aramid fibers.
What to ask when choosing strength members:
- What types of strength are required?
- Does this cable need to be rigid or flexible?
- What is the plan for connectorization and termination?
Multi-functional tubing
Breather tubes are necessary for maintaining functionality in certain extreme environments, offering enhanced protection against heat, abrasion, pressure, water, oil, chemicals, and flame. Breather tubes can be used to bundle inner components in wiring harness applications for protection and abrasion resistance, for gas and fluid transfer, and for dissipating heat, pressure, or steam.
What to ask when choosing breather tubes:
- What is the primary purpose of the tube?
- What secondary functions for the tube are desired?
- Will the cable be in high heat or wet environments?
- What material will best meet the needs of the application (polyethylene, nylon, polyvinyl chloride, polyurethane, or fluoropolymers)?
Water-blocking materials
Water-blocking agents react quickly to seal off any leaks and prevent liquid from migrating. Newer solutions allow for ease of installation and termination. They include dry yarns and tapes impregnated with water-blocking chemicals that activate when they come in contact with moisture to produce water-blocking gels and successfully trap and seal the leak.
What to ask when selecting water-blocking materials:
- Will the cable be partially or fully submerged?
- Are there moving parts or high flex requirements for the cable system?
- What types of liquid will the cable encounter?
Fillers for form and function
The primary function of filler material is to fill the space between components to create the desired form, but they can also be used to enhance functionality or add strength and protection against harsh environment conditions. Fillers are typically made of polypropylene, polyester, nylon, cotton, and paper that can be bundled, twisted, or layered. Each material offers specific benefits. For example, polypropylene rods add push and pull strength, polyester provides insulation, nylon resists heat, cotton will not melt in high temperatures, and paper has options for flame and moisture resistance.
What to ask when selecting filler materials:
- What is the desired form?
- How can filler enhance the cable’s function?
- What gaps could various filler materials address for this application?
Barriers: tapes, wraps, and separators
Barriers are mainly used to prevent the cable’s core components and the outer jacket material from bonding together. Configurations to isolate and separate internal components are highly customizable. Additionally, coverage can range from full to minimal depending on needs.
Some tapes, wraps, and separators can also perform additional functions.
- Aluminized backing can be used for shielding and insulation.
- Binder wraps hold components together to make sure tensions stay the same.
- Some tapes can increase flex life or rigidity. Others are specifically designed for high or low temperatures, or for use in any temperature.
- Wraps and tapes can be designed to protect cable or components from moisture and chemicals.
What to ask when selecting tapes, wraps, and separators:
- What internal components must be accommodated?
- What other functions would be helpful for this application?
- How will the cable be connectorized?
- Will the choice of material affect the connector housing?
Shielding for structural and signal integrity
Shielding protects the cable by increasing structural integrity and signal integrity. With the right materials and configurations, shielding can also add strength, flexibility, and noise suppression. Shielding is accomplished with aluminum foil tape; aluminized polyester tape; foil tape, braiding with tinned copper, stainless steel, bronze, and other materials; or drain wire. A combination of braid shields, which guard against low frequency noise, and foil shields, which guard against high frequency noise, is most effective against interference and maintaining signal integrity. Braiding styles are either box weave or spiral.
What to ask when choosing shielding:
- What type of noise interference will the cable encounter?
- What are the flex life demands for the cable system?
- What is the plan for connectorizing multiple shields?
Jacketing provides defense against harsh environments
The outer jacket is a cable’s main protection against environmental stresses and application demands. For medical and food grade applications, polyurethane, thermoplastic rubber, and polyvinyl chloride are used. Options for other applications include fluoropolymers, polyester elastomer, thermoplastic elastomer, and thermoplastic urethane. In some cases, a specialty blend is appropriate to meet specific, unique needs.
What to ask when choosing jacket materials:
- Will the cable be subjected to extreme temperatures?
- Is cut, crush, or abrasion resistance required?
- Are there low smoke, zero halogen (LSZH) requirements?
- Are there medical or food grade considerations?
Consider the connector
The connection is often the part of the assembly that is most vulnerable to the elements, so attention to terminating and connectorizing the cable is critical. The connector must have its own protection against the elements and operating conditions that exist in harsh environments: extreme temperatures or temperature fluctuations, chemicals, water, dust, sunlight, radiation, and more.
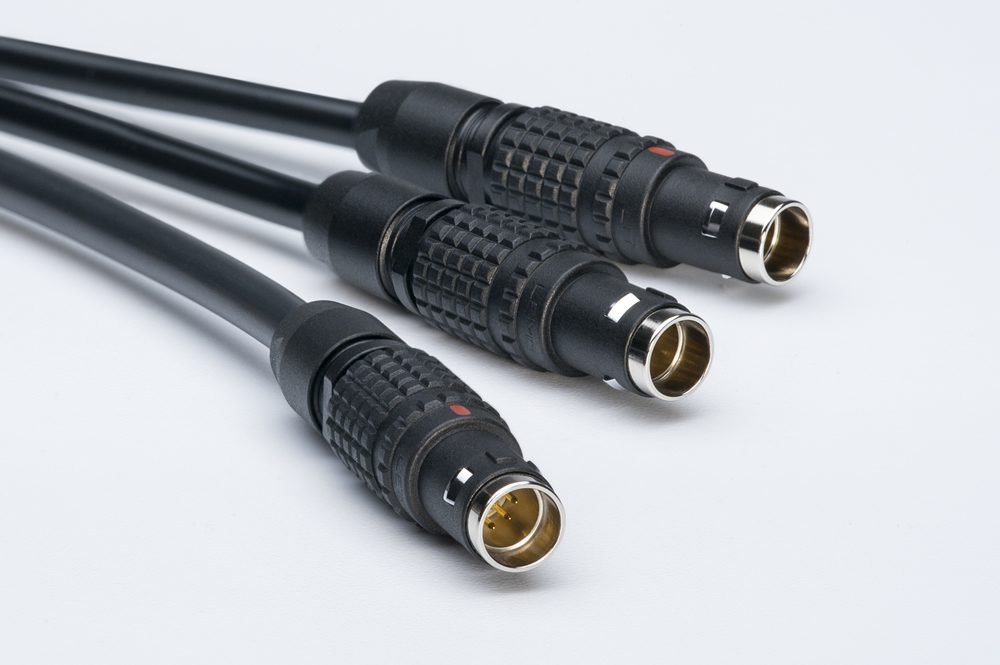

Waterproof IP68 LEMO T Series push-pull connector assembled with Northwire cable provides a rugged connectivity solution for many harsh environment applications. Push-pull self-latching provides quick operation and maintains a secure connection if cable is tugged.
Harsh environments often allow for only limited access and the connector and cable assemblies used in them may be expected to perform critical operations for decades. Whether in space, in a nuclear power facility, in medical equipment, or in a military application, someone is relying on that equipment to work as promised, so great care must be taken in the design, selection, installation, and operation of all the connectivity components.
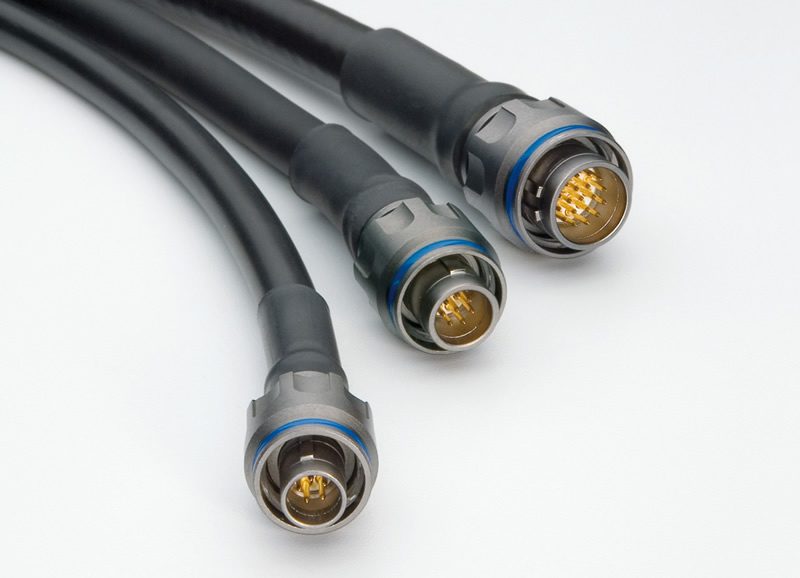

Waterproof IP68 LEMO M Series ratchet-coupling connector assembled with Northwire cable provides a rugged connectivity solution for many harsh environment applications. Ratchet coupling provides quick 3/4 turn to mate and de-mate and maintains a secure connection if cable is tugged.
Like this article? Check out our other articles on Cable, Cable Assemblies, our Wire and Cable Assemblies Market Page, and our 2023 and 2022 Article Archive.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- Top Questions to Ask When Selecting Cable for Harsh Environment Applications - February 28, 2023
- Effective Alternative to Silicone-Jacketed Cables and Cable Assemblies - April 12, 2022





