Automotive
Connector & Cable Special Topics
Consumer
Datacom/Telecom
Industrial
Materials
Medical
Military/Aerospace
Sensors/Antennas
Transportation Connectors
Wire & Cable Assemblies

Where in the World is Amphenol LTW's Luc Kan?
Amphenol LTW’s GM Luc Kan travels for work half of the year. Learn what keeps this connector entrepreneur and road warrior excited about technology — and how he stays serene while always in motion. Under the guidance of General Manager Luc Kan, Amphenol LTW has enjoyed a meteoric rise. Founded in 1993 as a waterproof connector specialist, the company quickly rose to prominence for…

Get the Latest News
Technical Expertise
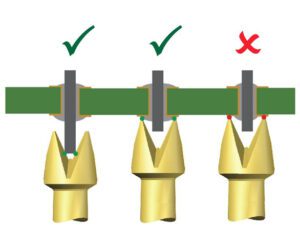
Selecting Test Probe Tips to Test Printed Circuit Boards
In-circuit and post-manufacture functional testing are critical steps to ensuring PCB dependability. Test probes provide the flexibility to make the electrical connections between the test system and the contact points on the PCB. Learn how to…

How to Select Electrical Connectors for LEO Satellites
The challenges of space are extreme: Outgassing, UV radiation, vacuum and oxygen conditions, and the unique harsh environment factors of low Earth orbit require careful consideration in component selection. Humanity launched the first rocket into space…

Building a Better EV Battery Monitoring System
New interconnect technologies help design more efficient, more powerful electric vehicles beginning with the battery pack. The foundation of any electric powertrain is the EV battery pack, as it is here that electrical energy supplied by…

The Universal Genius of M12 Connector Technology
When it comes to sensor and actuator applications, the M12 circular connector with A-coding is the first choice. Regardless of whether it is a matter of transmitting signals, data, or electrical power, M12 connectors have become…
Product Roundup

Medical Cable Assemblies Product Roundup
This week’s Product Roundup highlights medical cable assemblies from leading connector manufacturers and suppliers. Medical Cable Assemblies Avnet supplies circular MT optical cable assemblies from Molex. Today’s medical and industrial equipment generates vast amounts of data…
Mezzanine Connectors Product Roundup
This week’s Product Roundup highlights mezzanine connectors from leading connector manufacturers and suppliers. Mezzanine Connectors The Archer .8 series from Harwin has a 5 mm stack height. These cost-effective, dual-row 0.8 mm-pitch board-to-board connectors are intended…

MIL-Spec Rectangular Connectors Product Roundup
This week’s Product Roundup highlights rectangular MIL-spec connectors from leading connector manufacturers and suppliers. Rectangular MIL-Spec connectors Amphenol’s HDB3 rectangular connectors from Avnet incorporate a higher density contact pattern and lower mated height than Amphenol’s…
Automotive Connectors Product Roundup
This week’s Product Roundup highlights automotive connectors from leading connector manufacturers and suppliers. Automotive connectors Vishay high-current density TMBS eSMP rectifiers from Avnet are ideal for automated placement and feature Trench MOS Barrier Schottky technology (TMBS).…

High-Speed Cable Solutions Product Roundup
This week’s Product Roundup highlights high-speed cable solutions from leading connector manufacturers and suppliers. High-Speed Cable Solutions 3M Twin Axial PCIe Extender Assemblies for PCIe 4.0 applications, available from Avnet, is a family of cable assemblies…
Meet the Connector
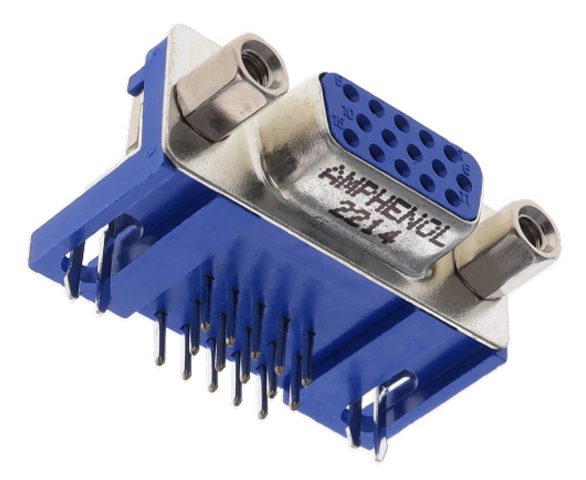

Meet the Connector
What is a VGA Connector?
What is a VGA Connector? Meet the Connector: VGA Connectors A VGA (Video Graphics Array) connector is a standard interface used to connect a desktop computer, medical monitor, signage display, projector screen, or other video-generating device to a monitor or display screen. The VGA interface is now considered…
Technology Trends