What is a Busbar?
Meet the Connector: Busbars
A busbar is a metallic strip or bar used to conduct electricity from a power source (such as a transformer or generator) to various electrical loads. Busbars provide connection points for electrical devices, such as circuit breakers, fuses, switches, and other components that are mounted directly onto the busbar or connected to it via bolts, clamps, or other means. They provide a low-resistance path for electricity to flow, minimizing power losses. In some cases, busbars are used to regulate voltage within a system by providing a stable electrical connection between different components.
Busbars are typically made of copper or aluminum to ensure high electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. They come in various shapes and configurations, including flat bars, rectangular bars, and tubular bars, depending on the specific application and current-carrying requirements. They have a large surface area, which helps dissipate heat generated by the flow of electricity.
Busbars are commonly used in electrical panels, switchgear, distribution boards, and other power distribution systems. They are an essential component of electrical infrastructure, facilitating the safe and efficient distribution of electrical power in buildings, industrial facilities and machinery, vehicles, data centers, and other settings. While there have been advancements in electrical distribution systems and technologies, busbars remain an essential component due to their efficiency, reliability, and versatility.
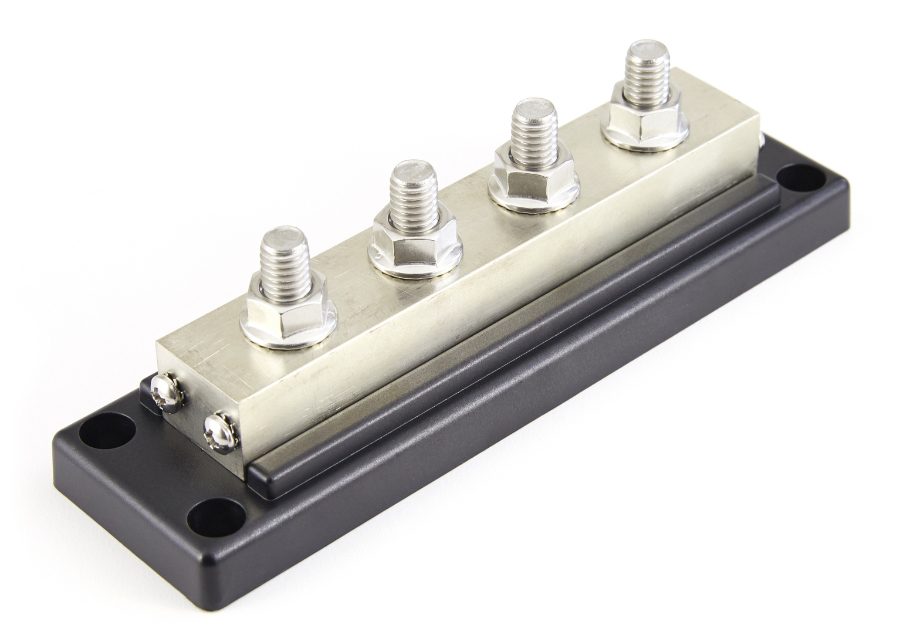

Blue Sea Systems 2104B PowerBar BusBar from Waytek features tin-plated copper and a reinforced polycarbonate base.
Design Notes
Standards: Depending on the type and configuration, busbars may subject to standards such as UL ratings and IEC 60050.
Materials: Copper, brass, aluminium. Plating may be used to increase contact resistance. Busbar materials are typically rigid enough to be able to support its own weight within a system. However, flexible busbars that are a much thinner construction may be specified for complex and high-current systems where heat fluctuations, magnetics, vibration, and other environmental factors are present. These busbars feature braided or strands of copper in a plastic or epoxy substrate.
Thermal expansion: Systems should be designed to accommodate the thermal expansion of busbars due to ohmic heating and system or environmental heat fluctuations.
Insulation: Some busbars are wrapped in insulation. They may also be installed on insulated supports.
Voltage: Voltage-carrying capacity varies widely depending on the application. At very high voltage ranges, connections around busbars may emit radio frequency interference, so designs should implement appropriate fittings to minimize this as well as related power losses.
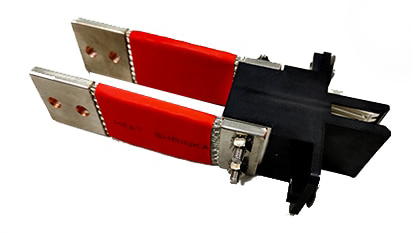
TE Connectivity’s flexible busbar handles high currents in a versatile, easy to install design.
Markets, Sectors, and Applications
Automotive, Datacom/Telecom, Test & Measurement, Medical, Industrial, and others.
Busbars are used in various industries, including automotive, electrical power distribution, telecommunications, data centers, and industrial machinery.

Weidmuller’s busbar product portfolio includes fork busbar and pin busbar versions with one to four poles. The cross-section and current of the electrical busbars are 10 mm² with 63 A or 16 mm² with 80 A.
Suppliers
Related products
- PCBs
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
- Power cables
Like this article? Check out our other Meet the Connector and Connector Basics articles, our Automotive Market Page, and our 2024 Article Archives.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- Where in the World is Amphenol LTW’s Luc Kan? - April 23, 2024
- TE Connectivity’s Sustainability Efforts Pay Off - April 23, 2024
- What is a VGA Connector? - April 23, 2024





