Connector Opportunities in Robotic Applications
Robots are rolling into new applications, from personal companions to an expanding industrial base. Their complexity and ranges of motion make rugged connectors a pivotal component.
 Mention robots to most people today and they think in terms of humanoids similar to those featured in movies such as Star Wars and ExMachina. Few would think that connectors are an enabling technology that helps designers add complexity and ensure that arms and other moving parts operate without failure.
Mention robots to most people today and they think in terms of humanoids similar to those featured in movies such as Star Wars and ExMachina. Few would think that connectors are an enabling technology that helps designers add complexity and ensure that arms and other moving parts operate without failure.
Amazing advances give robotic androids the ability to recognize nuanced speech, faces and text as well as understand and speak multiple languages. They can walk, run, carry heavy loads on uneven terrain and automatically recover from falls. Prehensile hands studded with sensors can handle fragile items with a soft touch. The majority of these advanced robots are developmental platforms and will likely serve only highly select applications including military surveillance, disaster rescue and bomb removal.
 An emerging commercial class of robots is being adapted with human characteristics to serve in social applications. Advanced companion robots linked to the internet are not designed to do work, but rather provide social contact and interaction. These devices are loaded with a variety of sensors that enable a remarkable degree of interaction with humans.
An emerging commercial class of robots is being adapted with human characteristics to serve in social applications. Advanced companion robots linked to the internet are not designed to do work, but rather provide social contact and interaction. These devices are loaded with a variety of sensors that enable a remarkable degree of interaction with humans.
Companion robots are in the very early stages of adoption with limited short-term component sales potential. These robots may utilize many types of sensors, motors, and actuators, but will be considered price-sensitive consumer products that will use low cost, commodity interfaces wherever possible.
A much larger potential market for components including connectors and sensors already exists in the rapidly growing market for robots used in industrial applications performing difficult, repetitive, intricate or dangerous tasks.
Today we are seeing all types of robotic applications that range from packaging food to cleaning up nuclear waste. Robots now have the ability to quickly learn new jobs and are now appearing in warehouses, hospitals and small businesses.
 One of the most significant advances in robotics has been in their ability to work collaboratively with humans. In the past, industrial robots were isolated from humans as their rapid movement and strength posed a serious safety hazard. Robotic work stations were gated or enclosed to prevent contact.
One of the most significant advances in robotics has been in their ability to work collaboratively with humans. In the past, industrial robots were isolated from humans as their rapid movement and strength posed a serious safety hazard. Robotic work stations were gated or enclosed to prevent contact.
Newer machines can directly assist humans and operate in “cage free” areas. Robots use a combination of limited force capability, multi-axis force and torque sensors as well as sonar and vision to detect human presence. This new breed of collaborative machines is being adopted by many smaller companies that can take advantage of the increased productivity that robotics can offer.
Robots are revolutionizing warehouse operations. Amazon utilizes a fleet of robots in their network of fulfillment centers to fetch and deliver product to human shippers, reducing delivery time and cost.
 Fixed robots are a growing market segment. Relatively low cost, table-top robotic arms, ideal for light-weight repetitive tasks, are rapidly expanding the range of applications for robots.
Fixed robots are a growing market segment. Relatively low cost, table-top robotic arms, ideal for light-weight repetitive tasks, are rapidly expanding the range of applications for robots.
Industrial robotic devices are highly complex electromechanical machines that may contain multiple computers, dozens of sensors, power management systems, multiple motors, hydraulic pumps, actuators and connections to a network. They often consist of many subassemblies which offer prime opportunities for small reliable and rugged interfaces. Connectors in these applications may be exposed to high temperatures, industrial fumes, dust, moisture, high-voltage spikes as well as excessive shock and vibration. Electromagnetic shielding may be required to protect sensitive signals from distortion.
As robotic devices have evolved from relatively few highly specialized devices to broad market applications, leading connector manufacturers have recognized the growth potential. Suppliers such as Amphenol Industrial, Harwin, LEMO, Molex, ODU USA, Omnetics, and TE Connectivity have created product micro-sites to promote connector product families applicable to robotic applications. Other suppliers including Anderson Power Products, HARTING, Hirschmann, Hirose, Phoenix Contact and Weidmuller offer market-specific brochures or feature products applicable to robotic equipment.
Connector Opportunities in Robotic Applications
In addition to standard interfaces such as circular military, commercial plastic and USB connectors, suppliers such as Molex have introduced new connectors specifically designed for use in robotic applications.
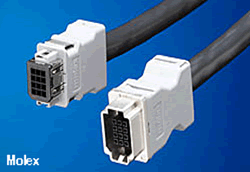 The Compact Robotic Connector (CRC) family from Molex is an example of a new connector that incorporates key features required in robotic equipment including power/signal contacts, positive latching, and a shielded housing.
The Compact Robotic Connector (CRC) family from Molex is an example of a new connector that incorporates key features required in robotic equipment including power/signal contacts, positive latching, and a shielded housing.
 The ROB connector from ODU features IP67 environmental sealing and resistance to extreme vibration.
The ROB connector from ODU features IP67 environmental sealing and resistance to extreme vibration.
 Omnetics developed their OmneMed plastic circular connector for robotic medical applications where high reliability and mating cycle life are absolute requirements.
Omnetics developed their OmneMed plastic circular connector for robotic medical applications where high reliability and mating cycle life are absolute requirements.
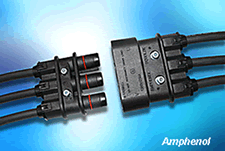 The RobiFix power connector family from Multi-Contact was designed specifically to address applications in robotic welding equipment where rugged, high-current sealed interfaces are required. It is rated to 180 amps and 1000 volts with a low-profile rubber housing sealed to IP67. Female contacts utilize louvered bands to reduce resistance and improve reliability. The Amphenol Industrial Products Group offers a similar connector with its RoboLok product.
The RobiFix power connector family from Multi-Contact was designed specifically to address applications in robotic welding equipment where rugged, high-current sealed interfaces are required. It is rated to 180 amps and 1000 volts with a low-profile rubber housing sealed to IP67. Female contacts utilize louvered bands to reduce resistance and improve reliability. The Amphenol Industrial Products Group offers a similar connector with its RoboLok product.
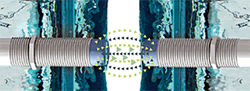 ARISO contactless interconnects from TE Connectivity is an ideal signal and power interface for a robotic arm where 360° rotation is required in harsh environments.
ARISO contactless interconnects from TE Connectivity is an ideal signal and power interface for a robotic arm where 360° rotation is required in harsh environments.
Expansion of industrial robotics will have some far-reaching social and political implications. A recent UN report indicated that up to two thirds of jobs in developing countries could be threatened by industrial automation. The impact in developed high-wage countries could be even greater. Introduction of new technologies often creates new job opportunities, but only for those who have applicable education or experience.
[hr]
Bishop & Associates recently published a detailed market research report that identifies robotics as one of ten disruptive innovative technologies likely to have a major impact on the electronic connector industry. Click here for more information on report M-760-16: The Impact of Disruptive Innovations on Electronic Interconnects.
Recently posted:
[related_posts limit=”10″]
- Optics Outpace Copper at OFC 2024 - April 16, 2024
- Digital Lighting Enhances your Theatrical Experience - March 5, 2024
- DesignCon 2024 in Review - February 13, 2024






