Vehicles Rely on FAKRA Connectors to Assure Performance
Today’s FAKRA connectors perform up to 6GHz and meet the rugged mechanical and environmental requirements of the automotive industry.
Higher Frequency RF Adds to System Complexity
Vehicles are incorporating an ever-increasing amount of telecommunications technology, ranging from data I/O to safety systems, that involves wireless connectivity for cellular, short range, and broadcast capabilities. These connected cars are communication hubs for control and external transmission, and challenge automakers to combine the requirements of the automotive industry — ranging from improved mileage and emissions to better crash resistance — with the fast-evolving cellular world.
Multiple coaxial lines in new cars will present the annual potential for tens of millions of connectors and cables. To help keep RF interconnection costs low and ensure high levels of electrical and mechanical performance in telematics applications worldwide, the automotive industry has standardized a family of relatively high-performance, cost-effective RF connectors based on FAKRA (Facharbeitskreis Automobil, a German organization of industry experts from vehicle manufacturers and equipment suppliers) and domestic USCAR (United States Council for Automotive Research LLC) standards.

Figure 1: A variety of FAKRA Connectors offered worldwide by Rosenberger.
Today’s FAKRA connectors perform up to 6GHz and meet the rugged mechanical and environmental requirements of the automotive industry in 50-, 60- (limited), and 75-ohm versions. These modified metal SMB connectors are embedded within a high-temperature plastic housing that’s color-coded for easy identification, with positive mechanical keying for 14 coding options (13 plus universal), and compatible with lead-free soldering. Additionally, to assure reliability, FAKRA’s locking system has both primary and secondary locking mechanisms to prevent inadvertent detachment. The FAKRA standards currently are DIN 72594-1/ISO 20860-1 and USCAR-17.*
Under USCAR, suppliers adhere to Electrical Wiring Component Applications Partnership (EWCAP), which includes standards for RF connectors. Automakers normally require components, including connectors, to pass the production part approval process (PPAP) — a lengthy process of documentation, validation, pilot runs, and demonstration of production capability — to assure the high-reliability performance required for commercial vehicles, which have the potential for major financial liability if a part’s failure could result in an accident or injury.
Major uses for FAKRA connectors include coaxial connections on devices with external antennas, such as: satellite digital audio radio services (SDARS), cellular communications, GPS navigation, keyless entry, and driver commands. For example, roof-mount antennas typically have short cables terminated with FAKRA connectors or bulkhead FAKRA connectors on the bottom to accept vehicle harnesses. A cable run is installed in the vehicle to route the signals, and the cables are terminated on both ends with FAKRA connectors. Multiple locations for FAKRA connectors are pictured in Figure 2.
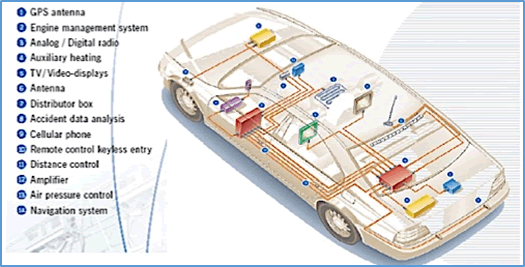
Figure 2: Automotive applications that commonly employ FAKRA connectors (Image courtesy of IMS Connector Systems GmbH)
FAKRA connectors also feature a unique and critical feature to help assure RF performance by permitting the connector’s central coaxial insert and attached cable to rotate a full 360 degrees. This prevents cable twist that could affect cable impedance and signal transmission integrity. FAKRA connectors were initially specified for 3-4GHz. However, the use of dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) for the safety sensors required for driverless or limited-drive vehicles,requires performance at 5.9GHz. DSRC is a two-way short- to medium-range wireless communications capability that enables very high data transmission required for communications-based active safety applications.
Prominent features of FAKRA connectors are described below and pictured in Figure 3.
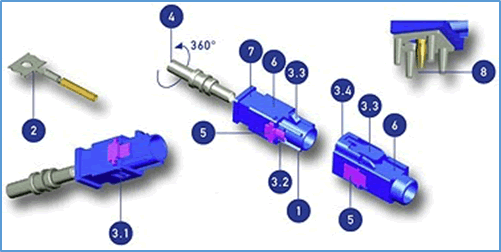
Figure 3: FAKRA connector features (Image courtesy of tech-support website: https://www.my-gti.com)
- Mating, with mechanical keying and a color-coding system with 14 different codes
- Continuous strip mounted, stamped-and-formed center contacts (usually on tape and reel) ensure efficient automatic assembly
- High mounting security:
3.1 Pre-assembling locking features ensure the correct position of the coaxial insert in the coded housing
3.2 Secondary locking feature prevents incorrect mating
3.3 Secure locking system between plug and jack with both tactile and audible mechanisms
3.4 Protection frame and protection strip protect against accidental demating - Coaxial insert and cable can be rotated freely 360° in coded housing
- Secure secondary locking with high axial retention force of the coaxial insert in the coded housing
- Shock- and vibration-proof housing protects the coaxial insert
- Cable types with fixing groove for chassis mounting
- Unique shape of inner contact ensures tilt-resistant PCB mounting
Designing for 6GHz usually involves transmission line studies (simulations) used for modeling microwave and millimeter wave connectors to assure that VSWR and insertion loss are minimized.
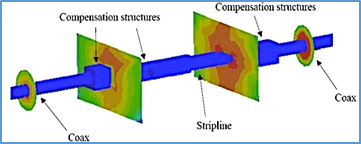
Figure 4: Images from a 3D electromagnetic simulation of FAKRA connectors (Image courtesy of TE Connectivity)
Originally specified for use with RF cables RG-174 and RG-316, FAKRA connectors are now available for a wider variety, including RG-58, RG-59, mini-59, RG-62, RTK-031, and LEONI Dacar® 037 cables. Due to international materials standardization, they are in accordance with RoHS2 (Restriction on Hazardous Substances Directive 2011/65/EU), and most meet requirements per the Directive on End-of-Life Vehicles (EU Directive 2000/53/EC).
Newer, enhanced versions of these products are known as FAKRA II, and are backwards compatible with original FAKRA connectors. Assemblies are available in single or multiple housing configurations for cable-to-cable, cable-to-board, or cable-to-panel PCB mounting via SMT or through-hole, and are harnessed to many other automotive connectors. Special options include moisture/splash resistance and sealing against water immersion to one meter. Amphenol also offers FAKRA-to-SMA adapters for expanded applications.
While simple cable assemblies can be terminated using manual tools, commercial high volumes and the need for inspection and confirmation results in the use of reeled contacts and automated termination plus 100% electrical test and SPC data collection.

Figure 5: TE Connectivity’s Alpha 356 auto-termination system for FAKRA II Connectors with stamped-and-reel contacts has seven stages for complex assemblies.
Standardized worldwide availability supports international supply chain needs. Suppliers include: Amphenol, ERNI Electronics GmbH, HUBER+SUHNER, IMS Connector Systems GmbH, JAE, Molex, Radiall, Rosenberger Hochfrequenztechnik GmbH, Samtec, TE Connectivity, and many others.
*Comment by D. Shaff, author: The original wording of this article inferred that USCAR-17 was being replaced by DIN and ISO standards. This reflected a sourcing interpretation related to “choice” of documents to reference and was not intended to state that USCAR-17 was being d ropped or canceled. Indeed, we have learned from Dr. Don Price, Leader – EWCAP Team, USCAR, who heads up the USCAR group overseeing this and related specifications, that an updated revision of USCAR-17 was released in December 2016. Those interested in automotive technology can review the extensive work underway by USCAR at https://www.uscar.org with applicable specifications including USCAR-17 listed at https://www.sae.org/servlets/works/documentHome.do?comtID=USCAR.
(Portions of this article are from the Section on Automotive Connectors in the World RF Connector Report issued November 2016 by Bishop & Associates.)

Recently posted:
[related_posts limit=”10″]
- New Circular Connectors Add to Multi-Billion Dollar Market - January 9, 2024
- Counterfeit Components Ground Airlines - December 12, 2023
- Cables, Connectors, Waveguides, and Hybrid Products for up to THz at IMS 2023 - July 11, 2023





