Six Common Connector Types Used in Medical Devices
Common connector types used in medical technologies are also specified for data centers, communications equipment, industrial systems, MIL-aero designs, and other high-reliability, high-performance markets.
Every component choice matters in the high-stakes design of medical devices and equipment. The electronic connectors specified for medical technologies aren’t always specific to this market, however. In fact, as medicine becomes more dependent upon audio/visual capabilities, high-speed data transfer, artificial intelligence, and real-time services such as remote guided surgery and home-based care, common connector types used for medical devices may be the same ones found in other high-reliability markets.
Major trends such as the growth of wearables have led to sensor data gathering, biocompatible and sterilizable materials, wireless data/power transfer, and smaller medical devices. AI is now being used for diagnosis. Remote telesurgery is performed with robotic arms. Advanced imaging systems instantly deliver detailed information to care teams. These trends command edge devices in which power density and processing capability are necessary in increasingly small form factors. For connectors, this translates to higher pin counts and power ratings.
Connector types such as board-to-board, wire-to-board, and wire-to-wire are widely used inside medical devices, and ruggedized versions of common USB, HDMI, and D-sub connectors add user-friendliness to these technologies. High quality versions of common connectors can also meet medical industry standards and regulatory compliance. Here are six common connector types for medical device designs.
1) Card edge connectors for medical equipment
PCBs with a series of pads along their edge can be inserted directly in the connector to interface with another system. Card-edge connectors are often used in computers as expansion cards, memory modules, or data acquisition (DAQ) cards to connect to a high-speed interface such as PCIe. In medical applications, they support complex computing and data analysis. For example, in a blood analyzer, DAQ cards in the A/D sample system collect and process incoming sensor data. In advanced patient-monitoring systems, card edge connectors are used to expand storage or test capabilities.
Card edge connectors used in medical devices must meet the highest quality parameters. Higher gold-plating thicknesses on contacts ensure that the more reactive base metal used in the pins does not oxidize and negatively impact conductivity. In high-vibration environments, connectors are susceptible to fretting corrosion where the rubbing that occurs at the metallic joints of a connection rubs off the plating as well as the underlying material ― a condition that worsens with time. This type of abrasion also occurs with frequent mating cycles. In medical environments, the potential exposure to reagents is also a concern. Selecting a card edge connector with thicker plating will mitigate these risks.
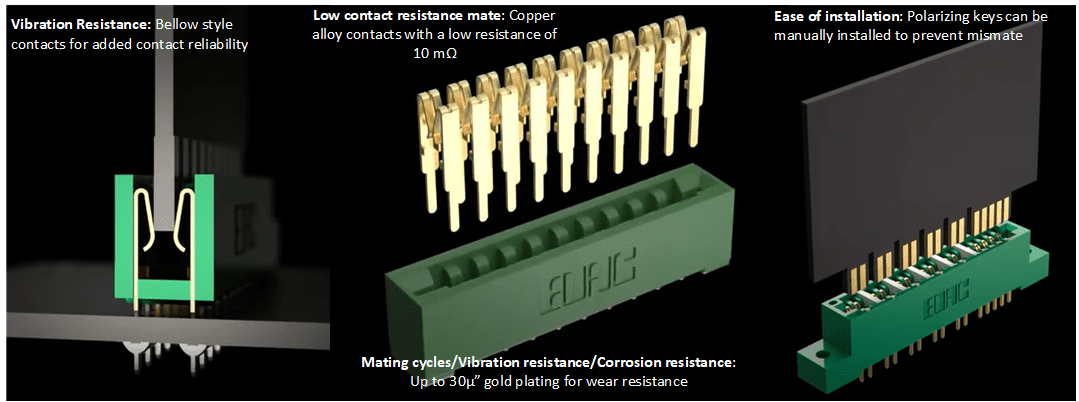
EDAC’s card edge connectors with bellow-style contacts provide a good contact spring force to resist vibration. After mating, a high-integrity connection is formed with the copper alloy contacts that have a lower resistance (at most, 10 mΩ). For additional vibration resistance, EDAC’s metal-to-metal card edge connectors have a high-reliability interlock mate with an innovative hermaphroditic contact design that utilize a fork-like shape that slides together for a gas-tight mate.
Another factor to consider is vibration, which can potentially worsen or interrupt a connection. Card edge connectors provide some elastic support in the event a circuit card is moving due to vibrations or transient shock.
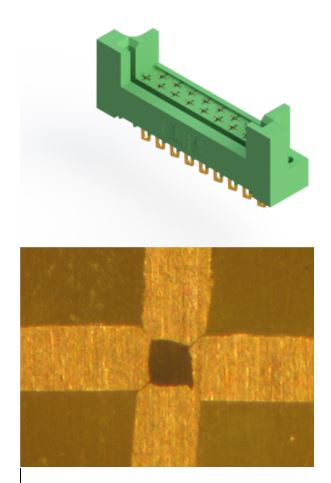
EDAC’s E-Met card edge connector with a hermaphroditic contact design and a cross-sectional view of the mate showing a gas-tight connection that can withstand vibration and shock.
2) Header connectors in multi-board solutions for medical devices
Header connectors are used for X-rays, CT scanners, ultrasound equipment, diagnostic cardiology equipment, MRI machines, heart-lung support systems, patient-monitoring systems, control boards going into blood analyzers, and more. Header connectors are used in all multi-board solutions to easily connect between boards. Typically, flexible cables such as ribbon cables are used for the cabling while headers are the connector heads. They are a reliable and cost-effective choice for wire-to-board and board-to-board connectors.
The high-conductivity copper alloy used in the pin connections offers both a low resistance and a better contact spring force. Adding up to 50µ” of gold plating can help resist corrosion and pin damage due to vibration. While a base material of UL 94V-0 thermoplastic polyester is used for an operating temperature range from -40 °C to 105 °C, other high-temperature materials can also be used for an extended temperature range. These durable connections can withstand a minimum of 200 mating cycles.
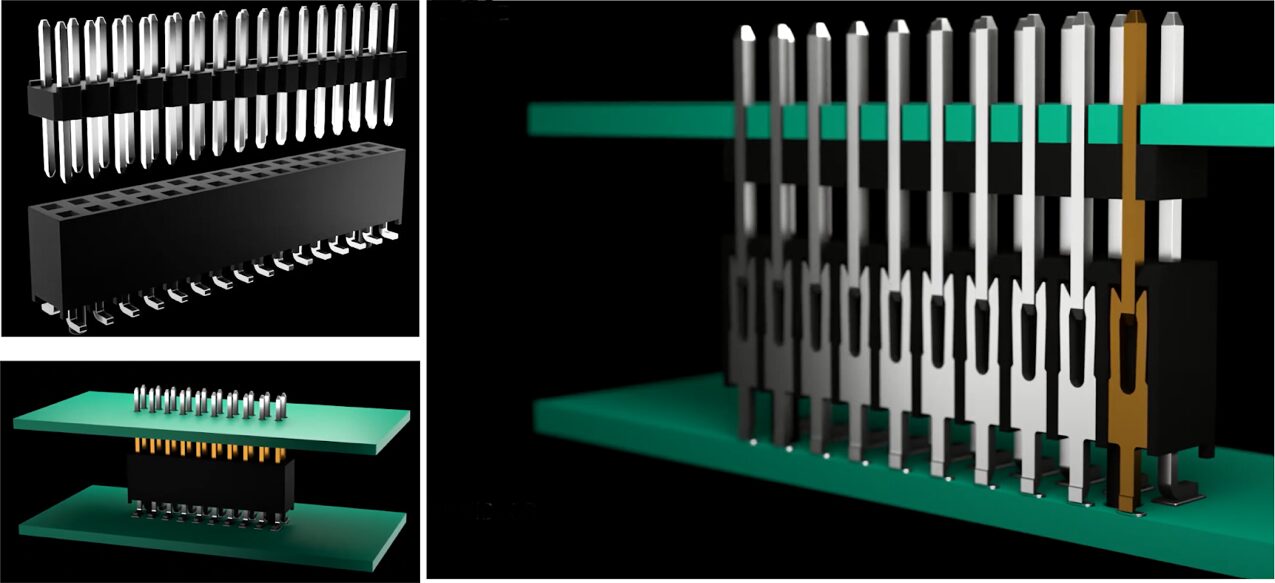
EDAC offers standard box headers as well as more specialized E-Socket and E-Pin headers, high-power headers, and DIN. Here, an E-Socket and E-Pin headers mate to form a vibration-resistant board-to-board connection. The fork design of the E-Socket receptacle can sufficiently grasp the E-Pin male connector with a maximum of 10 mΩ contact resistance.
For power connections between circuit boards, high-power headers offer up to 20 amps of rated current with integrated ground plane contacts that are offset from the power connections. The power pins themselves have a sizable pitch of 4 mm to mitigate the risk of arcing between contacts, thereby increasing the safety of the connection.
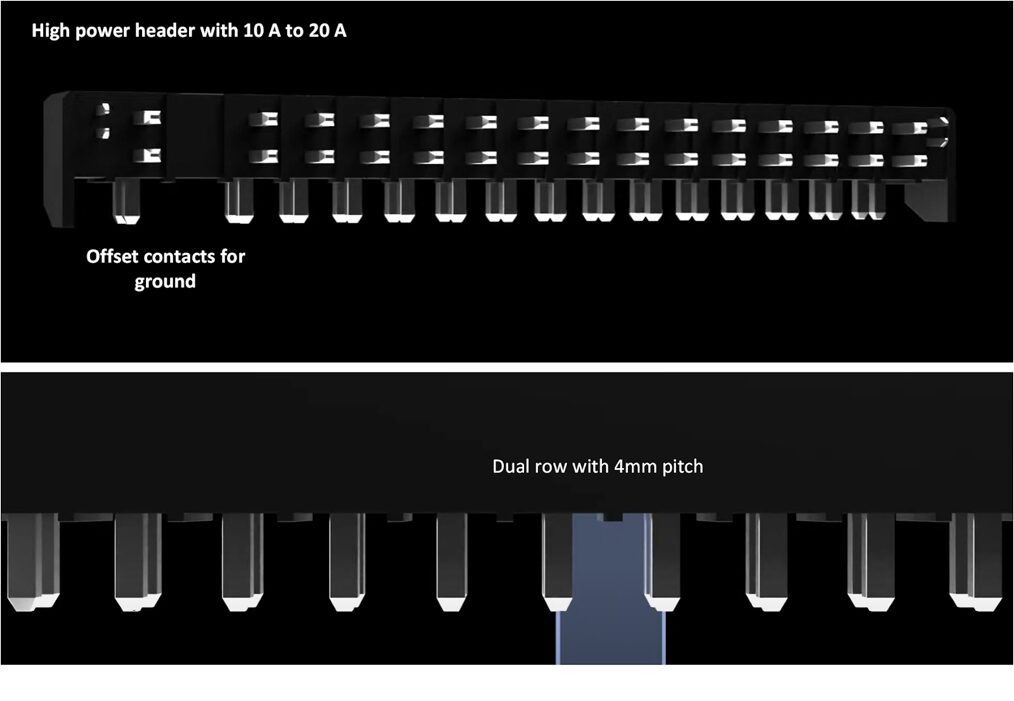
Power header connectors offer up to 20 amps of current with dual-row configuration and a 4 mm pitch.
3) In-line connectors in medical equipment
For some medical equipment, a wire-to-wire and wire-to-board solution such as an in-line connector may be necessary. In-line connectors have a relatively small pin count and are ideal for wire harnesses. In some medical environments, such as labs, in-line connectors may face exposure to fluids, a risk agent that causes moisture ingress and corrosion, which can lead to an intermittent or failed connection.
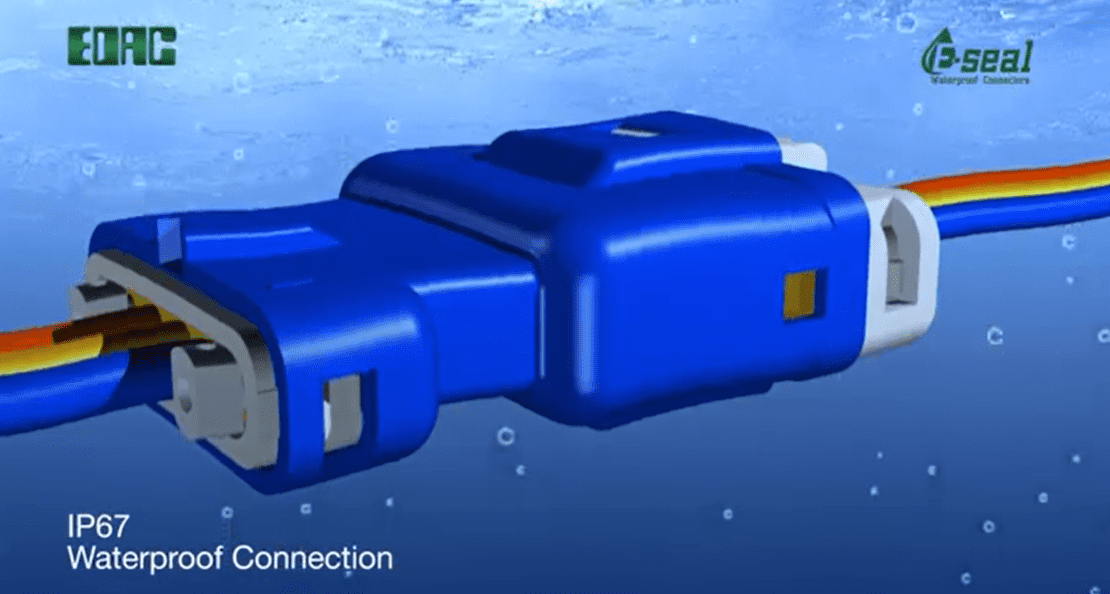
EDAC’s in-line connectors with E-Seal technology, a proprietary epoxy sealing process to seal the entire back of the connector rather than the individual pins, achieve an IP67 rating. They are completely dust-tight and can withstand temporary immersion in water.
4) D-Sub connectors in medical equipment
D-subminiature (D-sub) connectors are used across markets in applications ranging from personal computers to industrial automation controllers to aircraft connections. D-subs are widely used in medical technologies such as connections for sensors and actuators in monitors.
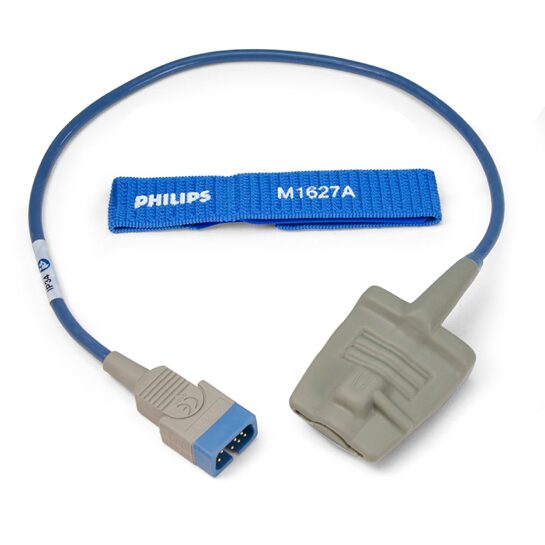

A D-sub connector connects pulse-oximeter probe in a defibrillator to measure oxygen saturation. Source: Philips
Constant vibration will deteriorate the quality of the connection over time. Sufficient gold plating and proper mounting can help mitigate these effects. D-sub connectors in medical applications should be IP-rated to prevent damage from dust and moisture.
Another consideration for D-sub connectors in medical applications is the potential for both radiated and conducted emissions (RFI and EMI), or noise. This noise can, for example, emanate from the machine’s internal power supply with high-speed switching devices. The cable can also conduct noise from other sources and bring that to sensitive internal circuitry and cause equipment malfunctions. D-sub connectors with metal shells, when connected to a chassis ground and to the shielding of a cable, can effectively mitigate EMI.
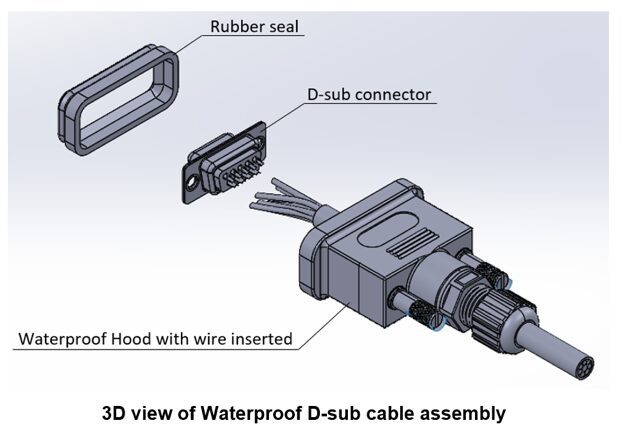
IP67-rated D-sub cable assembly with a waterproof hood and rubber seal. Metal hoods can also be used where EMI protection is critical.
5) HDMI connectors in medical equipment
HDMI connectors are the standard interface for all displays. Both D-sub connectors and HDMI connectors are used to feed video signals to computers or monitors to view images. Point-of-care ultrasound, for example, will use several video output options, including VGA, DVI, and HDMI, as well as legacy video outputs such as S-video or C-video. However, conventional HDMI connectors are not designed to withstand medical environments where vibration, mechanical shock, or moisture ingress may occur. EDAC’s waterproof HDMI connectors use E-Seal technology for resistance to splashes and potentially corrosive substances.

EDAC’s IP67-rated HDMI connectors feature E-Seal plus a quarter-turn twist-and-lock overmolding to protect the connection from vibration and shock.
6) Spring-loaded connectors for medical equipment
For wearable health monitors and other portable medical devices, user friendliness is critical when specifying connectors. Connector solutions for wearables, monitors, and home health devices need an easy blind mate connector with high durability for people of all skill levels to charge or dock their devices. Spring-loaded (or pogo-pin) connectors are easy to operate and can be adapted to fit medical applications as small as hearing aids for charging.
EDAC’s spring-loaded connectors feature a precision machined finish and magnets to provide polarization and increase the reliability of the connection. This makes them more convenient to use than standard pogo pins and enables them to maintain a connection even when vibration is a factor.
One factor that maintains a high vibration resistance is a spring-loaded connector’s stroke distance, the distance from the resting position of the pogo pin to its maximum compression position when mated. The stroke distance of EDAC’s pogo pins ensures that the connector can maintain reliable contact during vibration and during minor misalignments that would normally break a connection with standard contacts.

EDAC’s spring-loaded connectors can be adapted for testing/charging applications for wearables and medical device production. With a durability of up to 30,000 mating cycles, they can withstand frequent connect and disconnect cycles. They are assembled into a high-temperature thermoplastic for a wide operating temperature range.
While there are some application-specific connectors for medical technologies (e.g., a connector that mates to ultrasound equipment from the probe), the medical industry has adopted many common connector types. As long as they are ruggedized against rough handling and IP-rated to protect connections from ingress, these reliable and proven connectors serve medical devices well.
See more connectivity solutions for medical electronics at EDAC.
Read a use case in which card edge, header, and in-line connectors are implemented in a blood analyzer in EDAC’s article, “Engineering Considerations for Medical Connectors.”
Like this article? Check out our other How to Specify articles, our Medical Market Page, and our 2023 and 2024 Article Archives.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.