5G Wireless Networks and Connected Cars Advance Interconnect Technology
New connector families have evolved to meet increasing bandwidth and connectivity needs as the rollout of 5G and the era of advanced vehicle technologies approaches.
Wireless 5G and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies may eventually affect almost everything we do. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has prevented the mobile broadband standards organization 3GPP from meeting, which has slowed progress on the 5G Release 17 Specification. This release details new features and functionalities for 5G wireless networks and defines the second phase of deployment.

Many of us have experienced bandwidth limitations that restrict what we can do online, especially during times when many people are working from home. This has increased demand for 5G, which offers the increased speed and capacity required to accomplish compute-heavy internet-based business and leisure activities. 5G wireless networks will also present significant opportunities for transportation as vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technologies become part of our transportation and urban infrastructure. Driverless cars may be a ways off, although I’d welcome an automated vehicle to resupply my home during COVID-19 shutdown times. Vehicular 5G will involve almost-instantaneous information at gigabits per second (Gb/s) data rates and gigahertz (GHz) transmission frequencies far beyond most current levels.
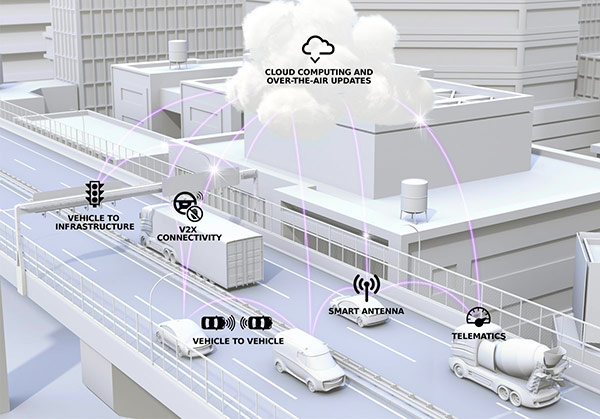
V2V and V2X capabilities will be realized with the full implementation of 5G wireless networks. Molex has developed a range of embedded connectivity solutions that will integrate vehicles with the urban environment.
New 5G wireless networks and existing/expanding fiber optic networks complement each other, offering better continuity across fixed and mobile applications in tandem than either could alone. 5G networks using coaxial cabling and wireless transmission will bridge the relatively short distances between mobile devices, including vehicle communications and businesses, with fixed 5G broadband and the long-distance fiber backbone. 5G wireless networks will use millimeter wave transmission to achieve the higher bandwidth needed to handle the projected communication requirements. Millimeter propagation usually travels only several hundred feet due to atmospheric attenuation. This short distance is causing telecom companies to switch from using a relatively limited number of large cell towers to thousands of small, low-power cell sites to transmit and receive signals from devices within each site’s small coverage area. In dense city areas, cell sites will be on almost every other rooftop and inside larger buildings and auditoriums. When the projections for vehicular communications are included, 5G will provide designers with significant opportunities to develop new products. Connector suppliers have developed several of the new products needed for this expansion.
Automotive applications for RF coax connectors in 2019 accounted for $745.6 million in sales, which was a jump of over 27% from 2018 as the new onboard and V2V/V2X systems began to come into use. These values are only for connectors and certainly would be multiplied several times if cable assemblies were included as well.
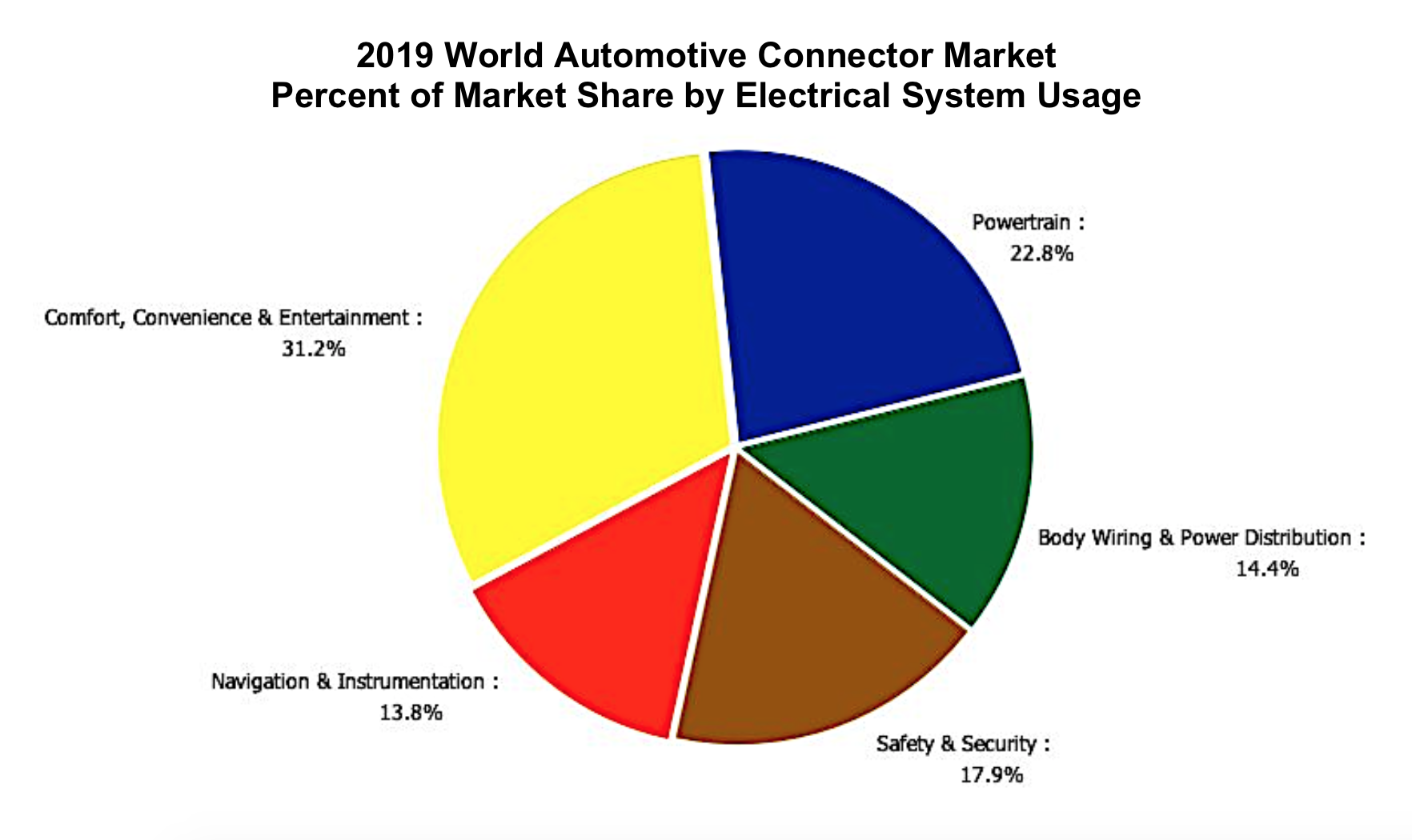
Before specific connectors are reviewed, let’s look at the size of the overall automotive connector market. Bishop & Associates calculates that the world automotive connector market for 2019 was $15.2 billion, broken down by usage in electrical systems as shown below:
In time, many status reporting and control functions for the new onboard V2V and V2X systems will be included in 5G data transmission. Implementation of 5G wireless networks is worldwide, based on international standardization, and many of the newer connectors for 5G applications are defined by DIN, IEC, and ISO standards, in addition to the United States Council for Automotive Research (USCAR) specifications.
FAKRA and FAKRA-Mini Connectors Provide GHz Transmission
Most vehicular data rates up to 6GHz can be handled by FAKRA connectors, which are based on the SMB connector interface. FAKRA stands for Facharbeitskreis Automobil, a German organization of industry experts from vehicle manufacturers and equipment suppliers. FAKRA connectors incorporate mechanical keying/coding for quick assembly with 14 coding options. They have primary and secondary locking features to prevent inadvertent detachment, plus color coding to differentiate between applications. The FAKRA standard is per DIN 72594-1 and harmonized with the USCAR-17 standard and ISO 20860-1.
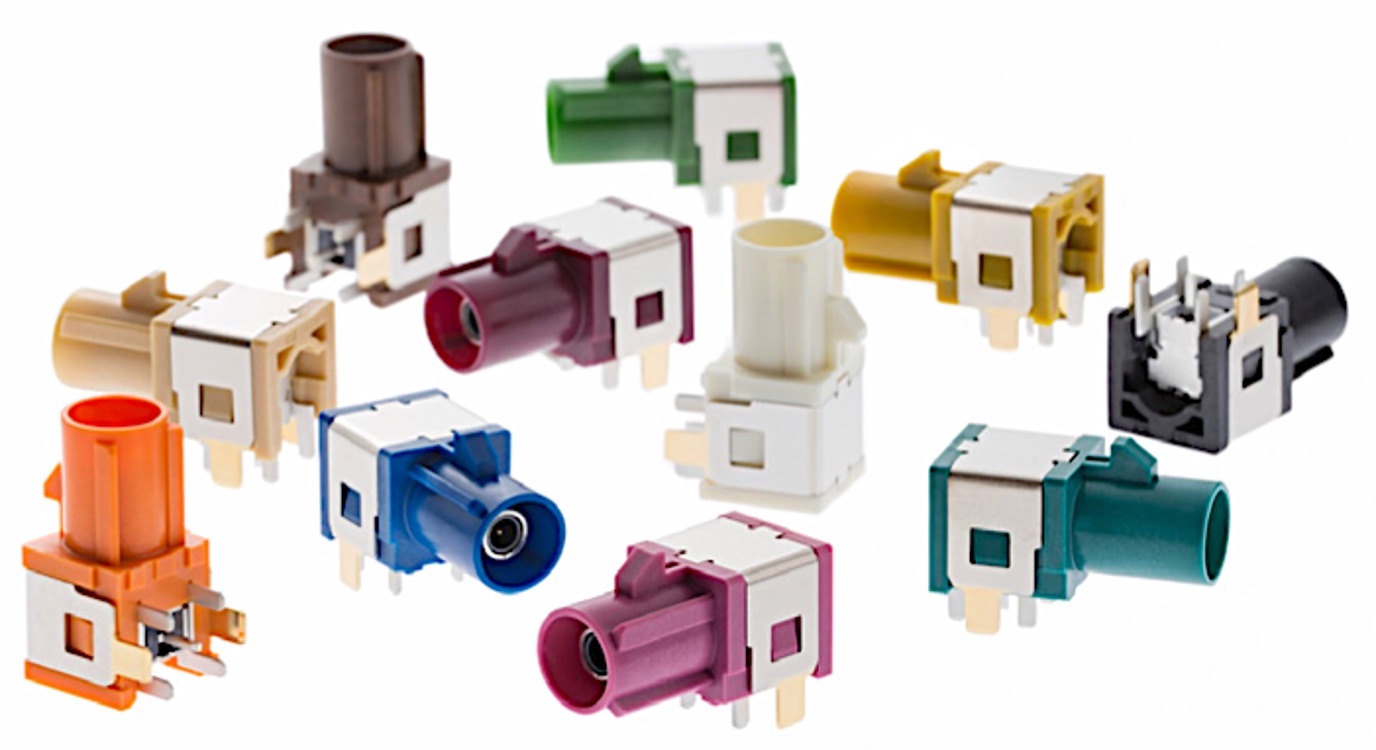

Mouser stocks Molex’s family of FAKRA Stamped-Body Connectors, which incorporate a lightweight design that’s suitable for a wide variety of automotive applications and are supplied on tape and reel for automated assembly.
Newer vehicle data rates involve transmission to 9.6GHz, and future applications will require even higher frequencies. This need is being met by next-generation FAKRA-Mini coax connectors. Initial efforts to ensure multiple sourcing were assured when Molex and Rosenberger announced a dual-sourcing agreement to produce Rosenberger’s HFM High-Speed FAKRA-Mini Automotive Connector System, which operates at frequencies up to 15GHz and supports the transmission of high-speed data rates up to 20Gb/s. In addition to providing higher frequency capabilities, FAKRA-Mini connectors also have a smaller, modular construction that offers more than 80% space savings versus conventional FAKRA connectors.
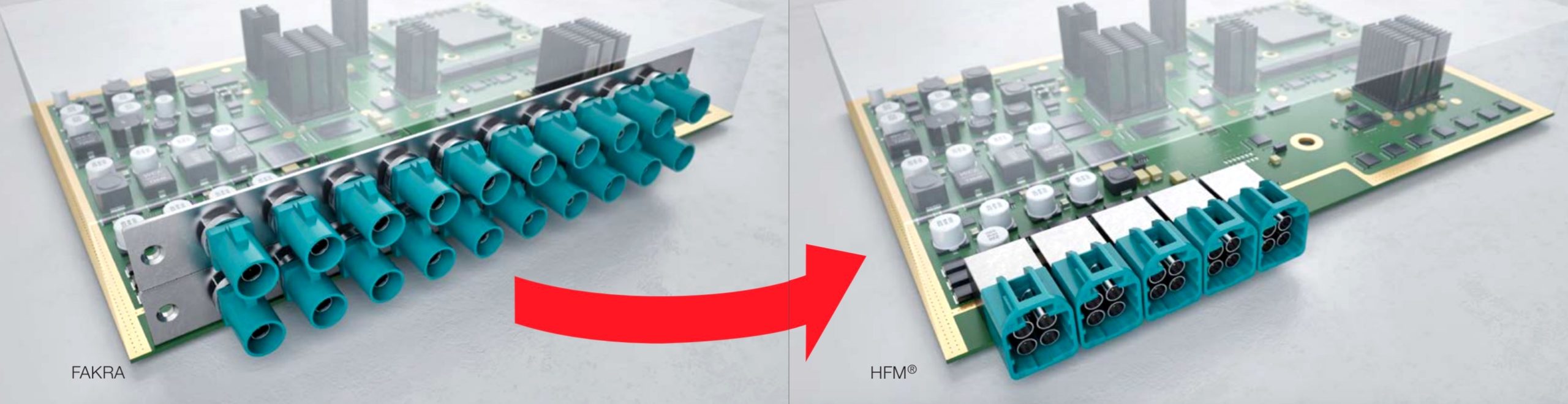
Scaled-down FAKRA-Mini connectors provide significant space savings, as shown in this Rosenberger diagram, which compares the board space occupied by 20 standard FAKRA connectors (left) to just five x4 HFM FAKRA-Mini connectors (right).
5G wireless networks in congested cities will require thousands of mini-transmit/receive boxes located near each other. Most installations will require two or more optically connected boxes. Cable I/O connectors include low-PIM versions of N-type connectors and larger 7/16 DIN and 4.3/10 Series connectors. With the need for miniaturization and higher frequencies, newer connectors will continue to be brought to market.
Commercial transports are already leveraging additional field data recording capabilities like GPS location tracking systems and transmitting that data back to their offices, and these systems often require reliable environmental sealing to protect cameras, sensors, antennas, connectors, and other components from moisture, dust, and other environmental hazards. While traditional sealed connectors such as SMA may be used, Molex and JAE offer FAKRA connectors sealed to IPX9K equivalent when mated, while TE Connectivity’s DEUTSCH product line and Aptiv (formerly Delphi) offer multiple vehicle connectors with various levels of environmental sealing for both antenna and other external vehicle applications. The transportation market trend toward higher frequencies with shorter wavelengths will also result in smaller vehicle antennas, which can be terminated with miniature coax connectors such as I-PEX’s MHF-TI or Hirose’s U.FL. series. Antenna transmission involves tracking via beam forming, steering, and tracking to handle 5G new radio (NR) transceiver and front-end RF components. Besides placement in rooftop fins, some antennas can be attached directly to vehicle glass and cabled to internal processors.
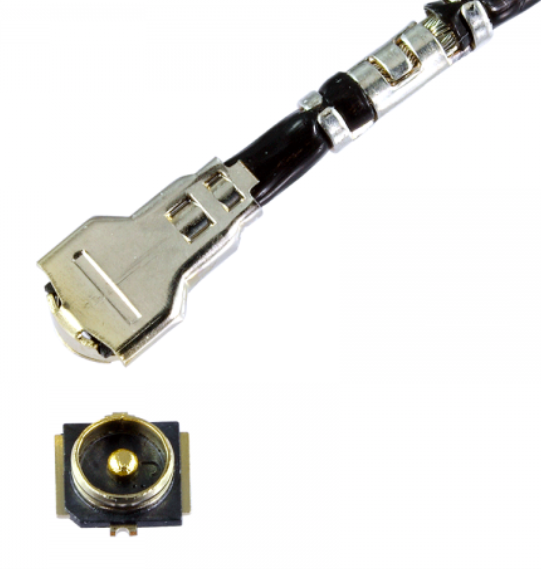

I-PEX MH4 cable- and board-mount connectors are well-suited to antenna applications.
New Coax Connectors Offer Size and Transmission Benefits
NEX10 is one of the latest families of connectors designed to meet the needs for new high-speed networks. Developed by members of the NEX10 Consortium, including Rosenberger, Radiall, and HUBER+SUHNER, NEX10 connectors are 50Ω, low-PIM coax connectors for small cells, distributed antenna systems (DAS), technology infrastructure for buildings, and multiple-input/multiple-output (MIMO) applications. NEX10 was submitted for IEC standardization in 2019. The increasing number of jumper connections per site has resulted in the need for multi-coax connectors, and NEX10 Multi Coax connectors are available with four or five NEX10 interfaces within a single connector housing that’s the same size as the popular 7/16 connector.
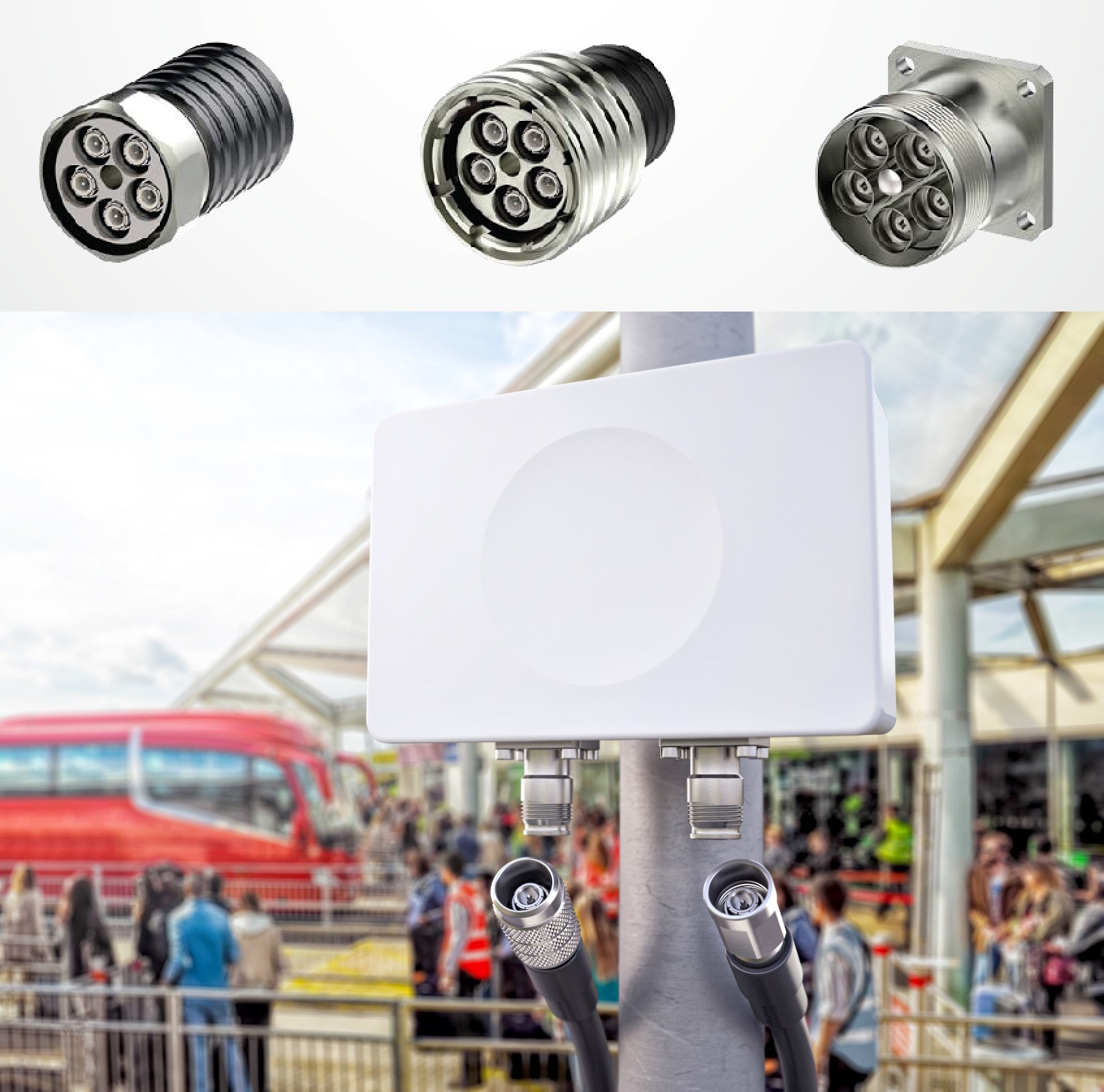

Rosenberger NEX10-5 connectors (top) in screw (left), push-pull (middle), and universal jack (right) configurations all feature a central guide pin that serves as a secondary alignment mechanism to ensure proper mating. NEX10 connectors are also available as field-installable cable assemblies (bottom).
Another new connector technology developed for mobile communication and forthcoming 5G applications is the DIN 2.2/5, which is about the size of a TNC but with electrical performance similar to 4.3/10 connectors.. Like NEX10, these connectors are intended to be used instead of larger 4.3/10 connectors in applications where reduced size is important. Connector companies involved with this specification include Molex, Amphenol, and Telegärtner. Standardization will be under IEC 61169-66. Although the design has a cutoff frequency of 26GHz, most near-term applications are expected to be in 6GHz to 8GHz range.
Continuing the trend towards miniaturization, the new 1.5/3.5 Series is another robust low-PIM connector for 5G small cell and other communication box applications. Telegärtner is the first company to offer this connector, which is similar in size to SMA connectors but requires 47% less space than the 2.2/5 Series and 75% less space than the 4.3/10 Series. In addition, despite their small dimensions, the new 1.5/3.5 Series connectors can transmit considerable power, up to 100W at 2GHz.

Telegärtner’s Cell IQ Family delivers maximum power in three compact sizes.
As requirements for processing speeds grow, frequencies will increase to ensure the best performance concurrent with maximum data transfer speeds. The short wavelengths of 5G wireless networks enable the use of small antennas and massive MIMO techniques to multiply wireless connection capacity. Precision is critical for the many connectors, cables, and circuits involved.
 The connectors presented in this article are a few of the more than 80 connector series included in the new Bishop & Associates report, “World RF Coax Connectors 2020.” This report presents the most up-to-date market information, trends, RF connector technology, products, and application information. RF coax connector sales for the years 2018, 2019, 2020F, and 2025F are provided by RF connector family and type, worldwide, and by regions of the world. Predictions include effects of trends for higher frequencies, broader application bandwidths, and international shifts. Click here for a detailed table of contents and ordering information for World RF Coax Connector Market 2020.
The connectors presented in this article are a few of the more than 80 connector series included in the new Bishop & Associates report, “World RF Coax Connectors 2020.” This report presents the most up-to-date market information, trends, RF connector technology, products, and application information. RF coax connector sales for the years 2018, 2019, 2020F, and 2025F are provided by RF connector family and type, worldwide, and by regions of the world. Predictions include effects of trends for higher frequencies, broader application bandwidths, and international shifts. Click here for a detailed table of contents and ordering information for World RF Coax Connector Market 2020.
Like this article? Check out our other New Technology, 5G, and Market Update articles, our Transportation, Automotive and Datacom/Telecom Market Pages, and our 2020 and 2019 Article Archives.
- New Circular Connectors Add to Multi-Billion Dollar Market - January 9, 2024
- Counterfeit Components Ground Airlines - December 12, 2023
- Cables, Connectors, Waveguides, and Hybrid Products for up to THz at IMS 2023 - July 11, 2023





