Eight Things to Know About M39029 Contacts
Commonly used in military, defense, industrial, and other harsh-environment applications, M39029 contacts are available in a variety of options. As a result, not every M39029 contact is created equal.
By Steve Smashey, President, and Mike Conte, General Manager, SOS Engineering, Inc. M39029
To manufacture a reliable, high-performance connector for harsh-environment applications, the design process should start with the contacts. The M39029 (SAE AS39029) specification includes requirements for crimp contacts to ensure durable and consistent signal transmission in demanding operating conditions. Commonly used in military, defense, industrial, and other harsh-environment applications, M39029 contacts are available in a variety of options. As a result, not every M39029 contact is created equal. Here are eight things to consider when specifying M39029 contacts.
1. M39029 Contact Materials
The M39029 specification simply states that the contact must be manufactured out of a copper alloy. However, this material specification is quite vague, as modern material sciences have produced more than 400 copper alloys. Copper alloys are metal alloys that have copper as their principal component. They all offer high resistance against corrosion, but other characteristics can vary. Well known copper alloys include bronze, where tin is added, and brass, which includes zinc. Brass is commonly sourced for sockets used in commercial applications. For harsh environments, leaded nickel copper or beryllium copper are ideal for their durability. Copper alloy materials can be selected based on the application requirements.
2. Tensile Strength
Higher quality materials inherently produce higher quality contacts with higher tensile strength and, as such, better spring properties. The M39029 specification states that contacts must be able to support a minimum of 500 mating cycles. Tensile strength is important for the reliability and durability of interconnects that serve applications with high mating cycles and long operating lives. High tensile strength ensures that female (socket) contacts will spring back into place after each mating and unmating cycle, and proper placement ensures reliable connectivity for the next mating cycle.
3. M39029 Contact Size
Contact size is also a consideration when choosing the material for M39029 contacts. Larger contacts usually have thicker walls, which helps to make sockets less susceptible to losing their spring properties. As a result, in many applications, large contacts can be made of lower quality, less costly copper alloy materials.
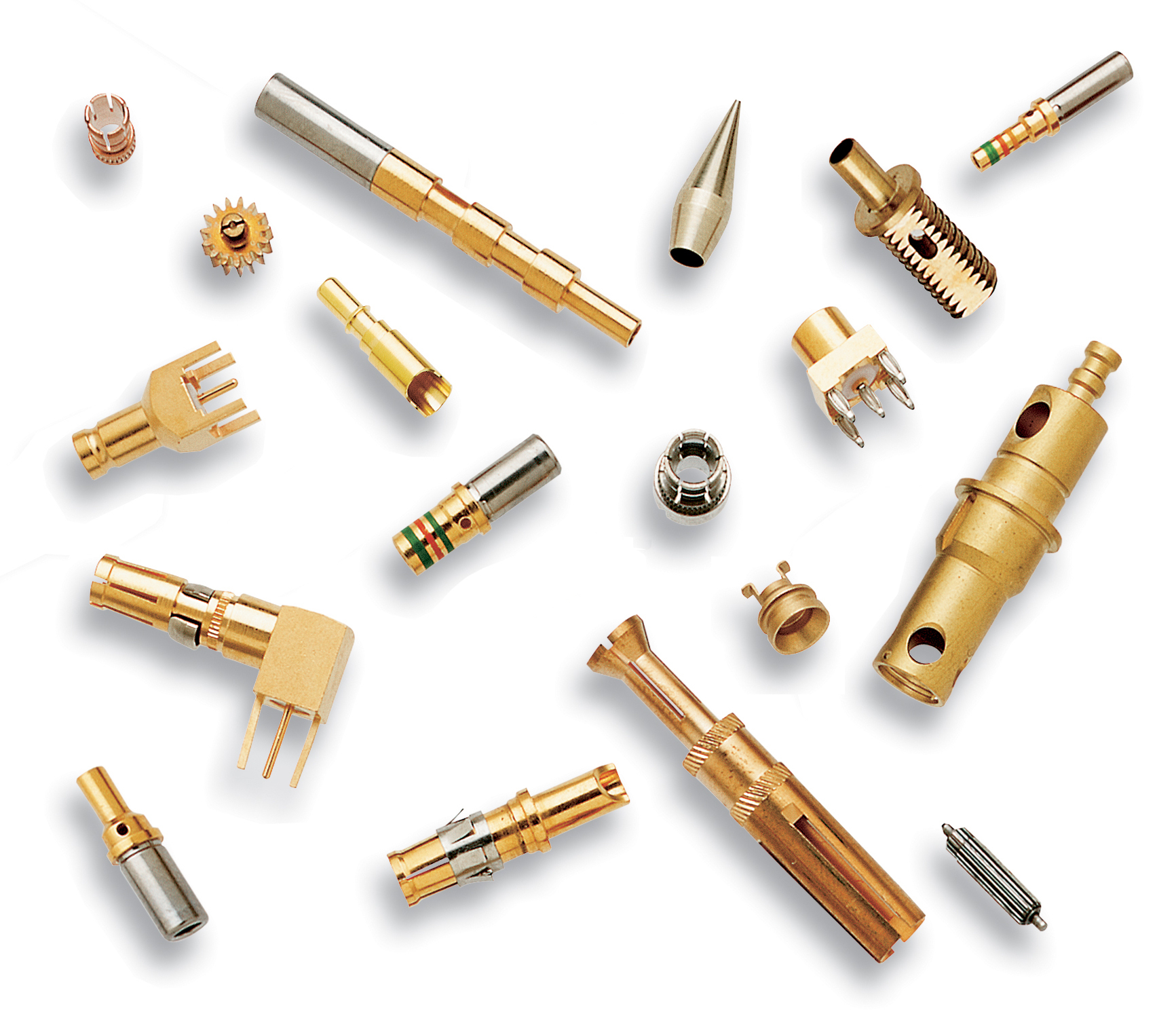

SOS Engineering designs and manufactures a wide range of precision turned metal parts, including M39029 contacts (as seen above with green and red stripes).
4. Zone Annealing
M39029 contact materials are also selected based on their ease of crimping. Crimping is the process by which two pieces of metal — in this case the contact and a wire — are joined together by deforming one or both of them to hold the other. This deformity is called a crimp. A special ratchet tool is often used to crimp connector contacts. The softer the metal, the easier it is to crimp. Contacts made out of harder copper alloys, like leaded nickel copper or beryllium copper, need to go through a process called zone annealing before they can be crimped. Zone annealing is a heat treatment process that makes the copper alloy softer. Zone annealing treatment reduces hardness to increase ductility and helps eliminate internal stresses and the chance for cracking during the crimping process. Softer materials like crimpable brass (i.e., CDA353000) do not need to go through the zone annealing process to be crimped and, as such, offer significant time and manufacturing cost savings.
5. M39029 Plating
Plating materials are also vital to the performance characteristics of M39029 connector contacts. Plating materials are chosen for several performance characteristics including corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, solderability, wear resistance, or operational life. Depending on application performance requirements, different types of metal or alloys — including copper, tin, gold, cadmium, rhodium, zinc, silver, nickel, and chromium — can be used in the plating process. Plating the contacts with a thin layer of gold provides the most valuable benefits. The M39029 specification mandates that gold plating be used due to its many exceptional performance characteristics, which include corrosion prevention, enhanced durability and reliability, increased heat protection, diminished fretting degradation, and excellent electrical conductivity.
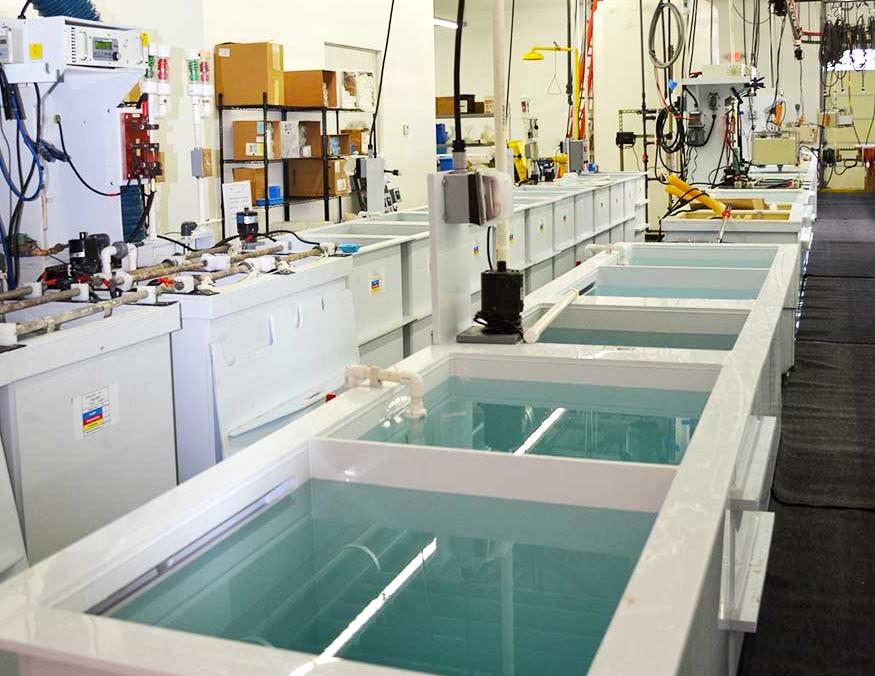

Contacts can be electroplated with various materials, depending on an application’s performance requirements and cost constraints.
The M39029 specification historically required 0.000050” of gold plating over the entire outer surface of the contact, but now allows for selective gold plating. Selective plating offers significant cost savings for M39029 connectors and can also target plating to critical areas, which increases the number of mating cycles by offering improving wear and tear resistance, more affordable. Gold-plated contacts are used in many harsh-environment applications to maintain low contact resistance over time since gold is resistant to oxidation.
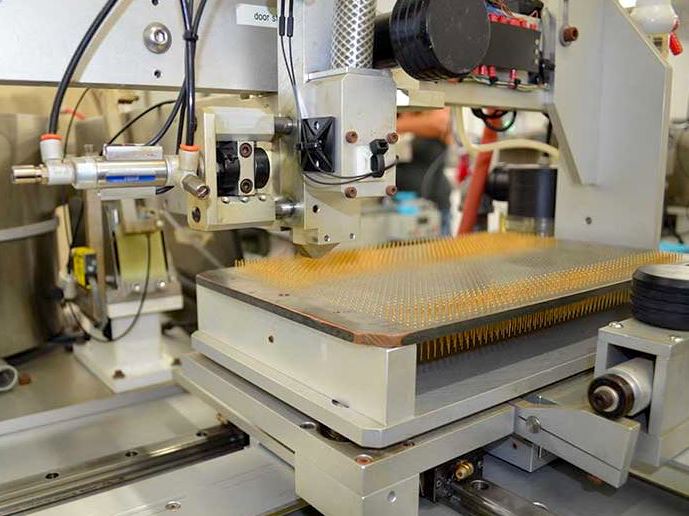

The M39029 specification now allows for selective gold plating, which offers all of the benefits of gold plating with significant cost savings.
6. Availability
The availability of copper alloy materials affects manufacturing in two significant ways. The scarcer a metal, the more difficult it is to source and purchase — even at expectedly higher costs. Some types of copper, specifically C97 (a low-alloy copper) and beryllium copper, can be difficult to source, which not only increases their cost, but also the lead-times for contact delivery.
7. QPL
M39029-certified contacts must go through a long, lengthy, and costly testing and approval process by the U.S. Government. Once approved, the product is listed on a Qualified Product List (QPL), which the government makes readily available to simplify specifying and sourcing processes. Although connectors used in military and defense applications must utilize M39029-certified contacts, non-military harsh-environment applications, including industrial applications, are free to use M39029 commercial equivalent contacts. These contacts can be just as good as, and sometimes even better than, M39029-certified contacts. The only thing that differentiates commercial equivalents from certified parts is that the contact manufacturer has not gone through the formal M39029 contact certification process. Using M39029 commercial equivalent contacts can provide connector manufacturers with an estimated 25–50% cost savings depending on the contact size.
8. BIN Codes
Batch identification numbers, or BIN Codes, are required on all M39029-certified contacts. BIN codes can include several different marks on the contact for identification purposes. Depending on the size of the contact, identification numbers can be stamped or rolled on or designated by a color code. This process adds time and cost to the manufacturing process as well. M39029 commercial equivalent contacts do not require this process, which again saves time and cost.
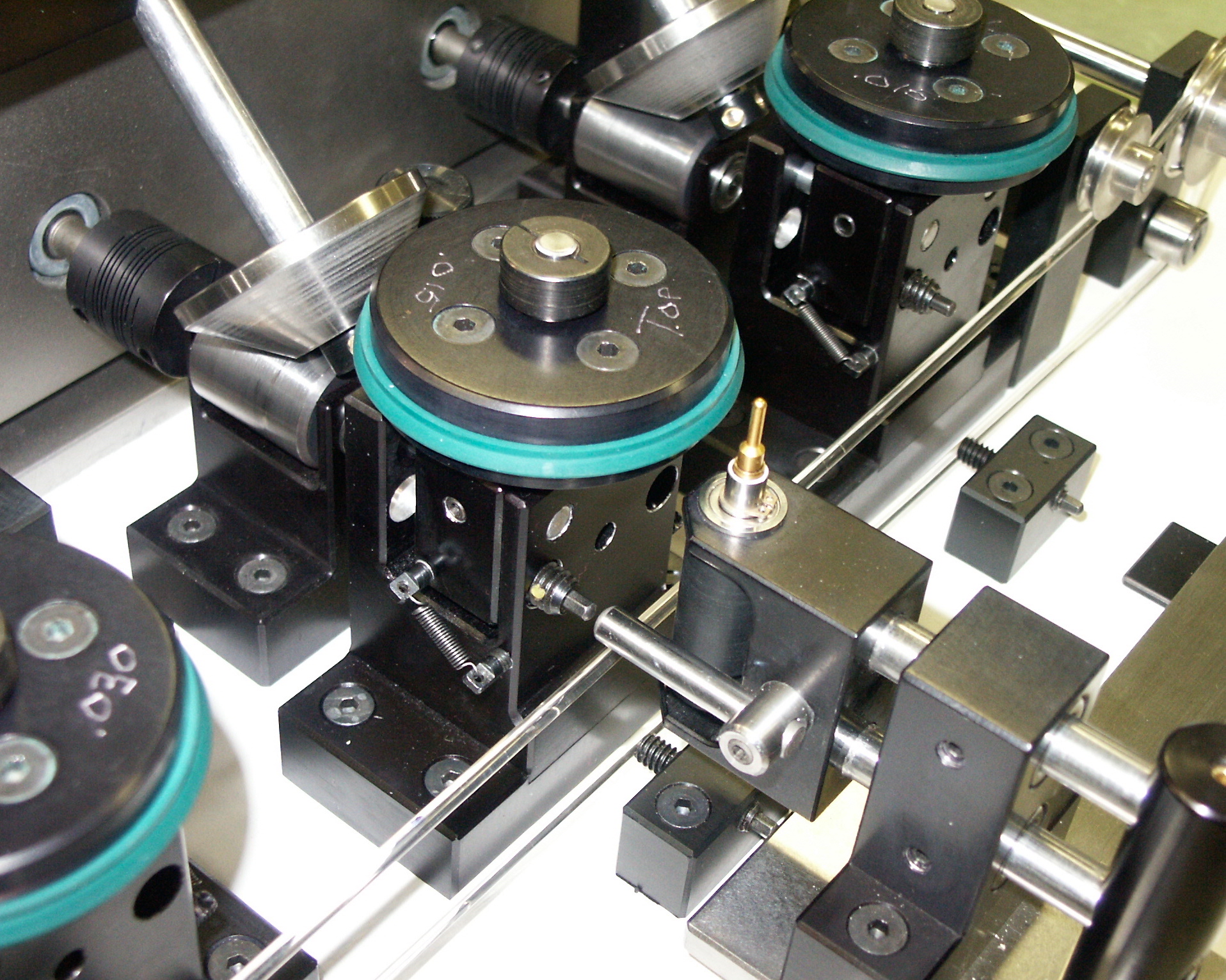

This BIN code machine marks M39029 contacts with color-coded stripes.
Conclusion
Contacts are the foundation for connectors and are essential to connector performance in the field. Connectors must offer predictable, repeatable, and application-appropriate performance characteristics. M39029 electrical contacts play a vital role to ensuring proper signal and reliability, and particularly so in harsh environments. Application requirements must be taken into account before selecting pin/socket and plating materials. If the application is not military or defense, a M39029 commercial equivalent may be an acceptable alternative to keep costs and delivery time down while maintaining reliable and durable performance.
Connector Supplier’s 2019 Mil/Aero eBook is now available! Expand your knowledge with this free collection of technical articles by leading industry experts, like this one from SOS Engineering. Download it here.





