Data Connectors for Tomorrow’s Robots
With the advancement of cobots, increased safety concerns, and the need to reduce downtime and costs, there is a much greater demand for networking automation in production facilities.
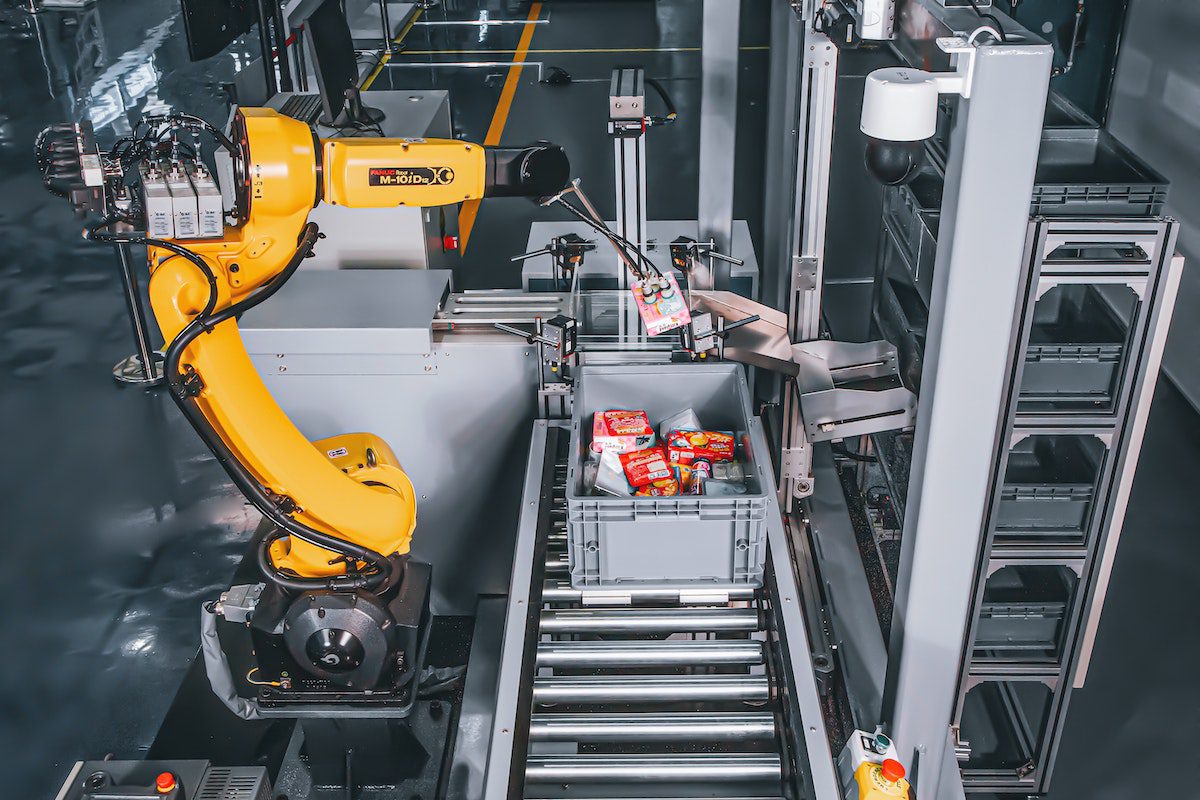

In today’s factory and warehouse environment, the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, collected, analyzed, and stored continues to grow. This trend is creating a need for hardware connectivity solutions that not only meet the traditional environmental and quality standards that have been in place for years, but also allow for faster, smaller, and more secure connections.
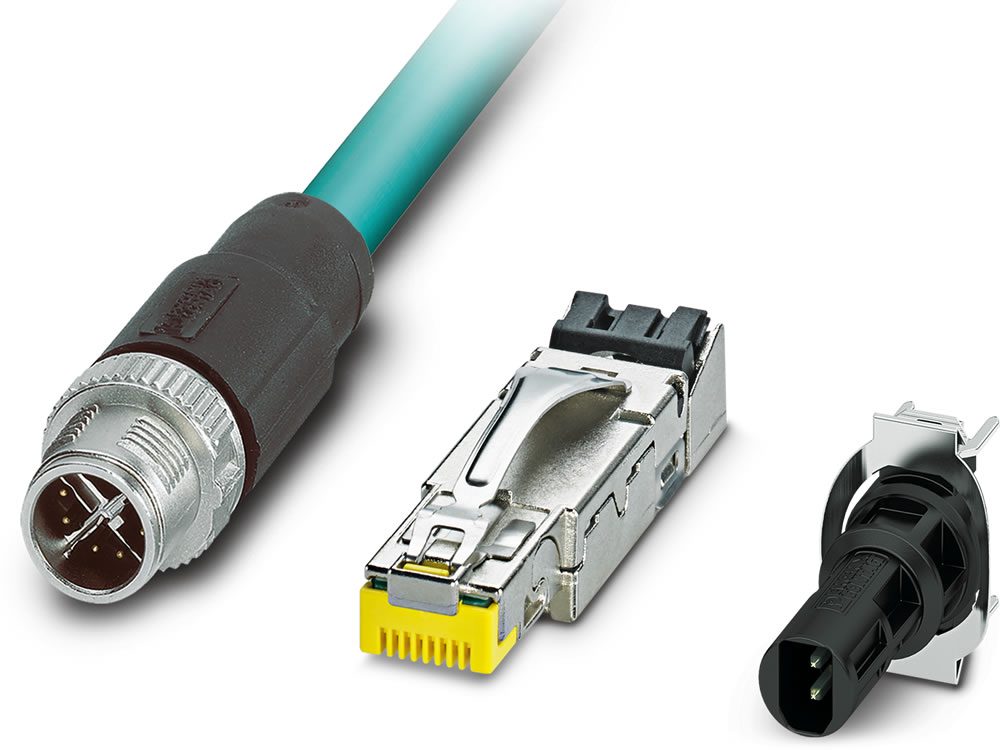
Robust data connectors for robotics applications have evolved and now come in many form factors, including M12, RJ45, and other options.
In most robotic applications on the factory floor today, Ethernet is still the most popular protocol used for networking and data collection. However, one can expect to encounter many other protocols such as EtherCAT, CC-Link, Modbus, DeviceNet, and CAN. As we look to the future, new technologies such as Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) will offer a wide range of advantages within this market space.
While each protocol has its place within a robotic system or network, they all have one thing in common: That is the need for reliable connectivity to function properly. The main factors to consider when specifying connector hardware for a data application include standards, speed, distance, environment, ease of use, power, dimensions, commonality among devices, wire termination styles, and materials. In some instances, the industry standard can dictate many of the requirements for a specific application.
An example to highlight would be Ethernet connectivity used in a factory floor robotic application. In this scenario, the need for shielding, vibration resistance, IP rating, and perhaps high-flex cabling will determine the direction one should look when choosing a quality connection solution. Many cables and connectors are available to meet these needs.
Industrial RJ45 Data Connectors
While newer form factors are emerging to unseat the de facto standard interface for Industrial Ethernet, the RJ45 connector has evolved to meet the robust demands of industrial applications like robotics. Gone are the simple, unshielded cables and basic PCB jacks. Instead, fully shielded cables with robust, high-flex sheathing provide reliable data transmission. Even field-wirable RJ45 plugs have left traditional crimp technology behind in favor of tool-less insulation displacement connectors (IDC). These connectors save significant installation time, are fully shielded, have an extended temperature range, and utilize special latch designs to maintain the connection when subjected to high vibration.
Even RJ45 jacks have been upgraded to include panel wings to establish a 360-degree shield; glass-fiber reinforced housing for higher temperatures; and an optimized design for plug retention. It’s easy to see why the Industrial RJ45 still represents a significant portion of Ethernet connectivity in robotic applications.
Options for Higher Currents
There are a couple of other interesting connector styles to review when searching for the right communication connector in a robotics application. In industrial settings, RJ45 connectors are suitable connectors for many data applications. However, their current carrying capabilities are limited to around 1.7 A, and some applications that rely on Power over Ethernet (PoE) require higher currents. In addition, it is always a good idea to include shielded connectors in applications with potential electromagnetic interference.
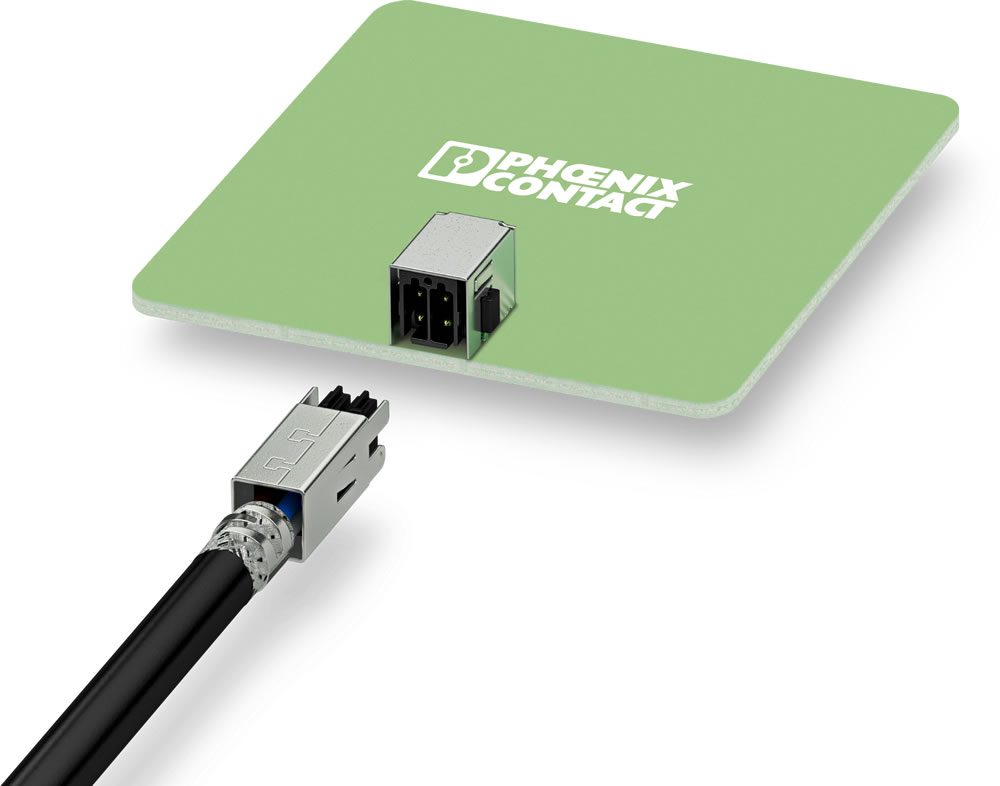

Shielded PCB connectors, such as the DMCC from Phoenix Contact, offer a reliable solution for Power over Ethernet applications.
Shielded PCB connectors offer a reliable solution for PoE applications. Due to their electromagnetically compatible shielding, connectors like this enable the reliable transfer of data — up to 100 Mbps — and power to devices. Gold-plated contacts ensure that data transfer quality remains stable over the long term, and a double row orientation allows for high density in a compact area. Crimp contacts are available on a carrier strip for easy and cost-effective termination, and are designed for currents up to 6 A at 10 V. Tooling is available for manual contact termination, or automatic tooling can be used for high-speed termination.
Circular M8 and M12 form factors are growing rapidly in acceptance for Ethernet connectivity, specifically the D-coded variants. IEC and IEEE standards help ensure desirable traits like cross-manufacturer compatibility, Fast Ethernet, and PoE are all possible. These circular form factors are far more robust, including environmental protection, compared to non-industrialized RJ45 jacks and corresponding plugs. In addition, inserts and cables can be color-coded to distinguish the various protocols commonly used in these robotic applications.
These form factors also offer options when connecting inside the control panel. These options can include going directly to a PCB; individual wiring; cabled solutions for maintaining shielding; and even cabinet feed-throughs. In fact, one common cabinet feed-through option converts from an M12 connection for field connectivity, thus maintaining ingress protection, to an interior RJ45 jack connection for easy assembly within the cabinet. Circular connectors are already commonly used for sensor connectivity. It makes sense that they would be readily accepted when it comes to data connectivity as well.
Over the next few years, the robotics market will continue to grow exponentially. These complex processes will require high volumes of data at faster speeds, but applications can vary widely based on a system’s unique requirements. Fortunately, connector manufacturers are keeping pace with the changes and offering many solutions to meet the high demands of the automation industry.
Learn more about connectivity solutions for robots at Phoenix Contact.
By Ken Horlacher, Solutions Engineering and Market Development Manager; James Dunbar, Senior Product Marketing Manager – PCC; Product Marketing Manager – Field Device Connectors; Phoenix Contact USA
Like this article? Check out our other Ethernet and RJ45 connectors articles, our Industrial Market Page, and our 2022 Article Archive.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.





