What are USB connectors?
Meet the Connector: USB connectors
USB gained popularity due to its compatibility with numerous platforms and operating systems, its low implementation cost, and its ease of use. The connectors are available in a variety of shapes and sizes with an array of features.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an industry standard developed in the 1990s for connections between computers and peripheral devices. USB gained popularity due to its compatibility with numerous platforms and operating systems, its low implementation cost, and its ease of use.
USB-IF (Universal Serial Bus Implementers Forum Inc.) is the support organization and forum for the advancement and adoption of USB technology. It was founded by companies that developed the USB specification and has over 700 member companies. Apple, HP Inc., Intel Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Renesas Electronics, STMicroelectronics, and Texas Instruments are currently represented on the board of directors.
Each USB connection is made using two connectors: a socket (or receptacle) and a plug. The USB specification addresses the physical interfaces and protocols for connection, data transfer, and power of devices. USB connector types are referred to by letters (A, B, and C) that indicate the physical shape of the connector and numbers (e.g., 2.0, 3.0, 4.0) that indicate the speed of data transfer. The higher the number, the faster the speed.
Specification – the letters
USB A is thin and rectangular in shape. It is probably the most common type, used to connect to laptops, desktops, media players, and game consoles. They mainly are used to allow the host controller or hub device to provide data or power to smaller devices (peripherals and accessories).
USB B has a square shape with beveled corners on the top. It is used for printers and external hard drives to send data to the host device.
USB C is the newest type. It is smaller with an oval shape and rotational symmetry (it can connect in either orientation). USB C transmits data and power on a single cable. It has been widely accepted and the European Union will require its use for battery charging beginning in 2024.
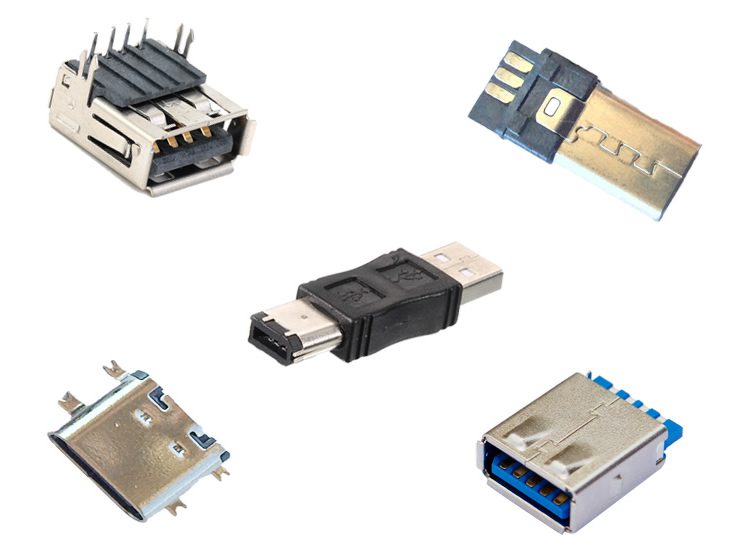

Greenconn offers a comprehensive range of USB connectors like Type-C, Micro USB, Mini USB, which provide horizontal or vertical sockets or plugs and can be installed in different ways suitable for I/O applications in various consumer and mobile devices.
Specification – the numbers
USB 1.0 (12 Mb/s), the original specification, was released in 1996 and USB 2.0 (480 Mb/s) came out in 2000. Both applied to USB Type A connectors.
With USB 3.0, the naming conventions get more complicated.
The USB 3.0 (5 Gb/s) also known as USB 3.1 Gen 1, came out in 2008. It is currently known as USB 3.2 Gen 1 and works with USB Type A and USB Type C connectors.
USB 3.1 or USB 3.1 Gen 2 (10 Gb/s) followed in 2014, currently known as USB 3.2 Gen 2 or USB 3.2 Gen 2×1, it works with USB Type A and USB Type C.
USB 3.2 Gen 1×2 (10 Gb/s) works with USB Type C. This is the most common specification for USB Type C connectors.
USB 3.2 (20 Gb/s) arrived in 2017 and is currently known as USB 3.2 Gen 2×2. This works with USB Type C.
(USB 3.0 is also known as SuperSpeed.)
USB4 (typically, written with no space before the 4) came out in 2019 and was in widespread use by 2021. The USB4 standard is up to 80 Gb/s, though today its maximum speed is 40 Gb/s. USB 4 works with USB Type C.
A Variety of Shapes, Sizes, and Features
USB connectors are available in standard, mini, and micro sizes, as well as in different connector styles, such as circular connectors and Micro-D versions. “Many companies produce connectors that meet the USB data and power transfer requirements but use special connector shapes to meet further requirements such as shock, vibration, and water ingress sealing,” explained Eric Bergquist, project engineer, Omnetics Connector Corporation. “For USB 3.0, extra connections were added to increase data transfer speed, which explains the changes in shape.” While meeting the data and power transfer requirements, however, these will not mate with standard USB connectors.
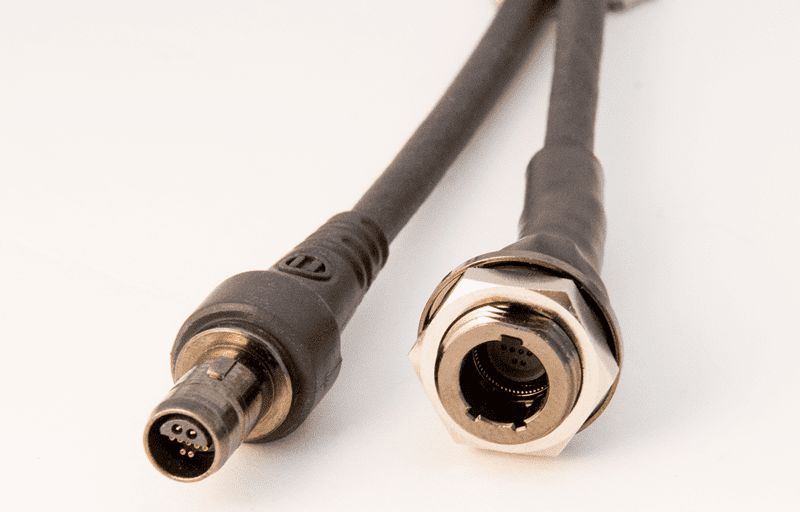
Omnetics Nano 360 USB 3.0 connectors provide reliability and ruggedness while passing the signal requirements of USB 3.0 (USB 3.1 Gen 1). Using both simulation and measurement, Omnetics maximized the performance for USB by optimizing the pin locations of the critical signals. This yields maximum data transmission and provides excellent crosstalk that meets the requirements of USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1.
Applications
Personal computers, keyboards, mice, cameras, printers, scanners, flash drives, smartphones, game consoles, wearable and portable devices, heavy equipment, automotive, industrial automation, and marine.
Suppliers
Omnetics Connector Corporation, Amphenol LTW, Greenconn, TE Connectivity, Molex, Amphenol CS, Bulgin Components, RS, Würth Elektronik, NorComp, GCT
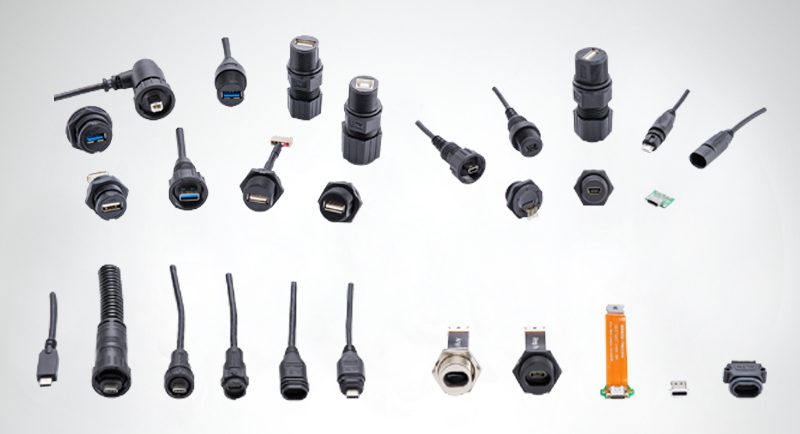

Amphenol LTW offers a comprehensive range of USB connectors designed to meet various application needs, such as heavy equipment and wearable devices, while providing versatile solutions for data and power transmission in challenging environments. The USB connector series includes Type A 3.2 Gen 1, 2.0, Type B 2.0, Type C 3.2 Gen 1/Gen 2, Mini USB Type B 2.0, and Micro USB Type AB, covering a wide array of connectivity options for different devices. These connectors come in different mating styles. They are salt spray and UV resistant, and feature IP67/IP68 ratings with reliable waterproofing that makes them highly effective in preventing moisture and dust ingress. Thermoplastic materials ensure durability and resistance to environmental factors. Supporting data transmission speeds of up to 10 Gb/s, these connectors ensure high-speed performance and seamless, efficient data transfer.
Like this article? Check out our other Meet the Connector and Networking articles, our Consumer Electronic Market Page, and our 2023 Article Archive.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- Sealing Success: Overmolding for More Secure Connections - April 23, 2024
- Medical Cable Assemblies Product Roundup - April 23, 2024
- Mezzanine Connectors Product Roundup - April 16, 2024






