Mold Presses – Fully Automated Encapsulation of Cables
Mold Presses – Fully Automated Encapsulation of Cables
 In today’s high-end production landscape, individual technical implementation of fully automatic manufacturing processes is becoming increasingly important. Decreasing unit numbers and production lifecycles, along with production requirements that are becoming more complex, define the scenario. Intelligent and efficient communication is required within equipment as well as between systems and personnel. But despite this increasing complexity, programming must be kept simple and reliable.
In today’s high-end production landscape, individual technical implementation of fully automatic manufacturing processes is becoming increasingly important. Decreasing unit numbers and production lifecycles, along with production requirements that are becoming more complex, define the scenario. Intelligent and efficient communication is required within equipment as well as between systems and personnel. But despite this increasing complexity, programming must be kept simple and reliable.
A current example is a highly compact production cell for the fully automated encapsulation of cables of varying lengths, which is equipped with a control system with graphic-based sequence programming for the injection molding machine, as well as for the six-axis robotic system. The resulting benefits include flexibility, short cycle times, and a high degree of availability.
Automation: Complex, Compact, and Extremely Flexible
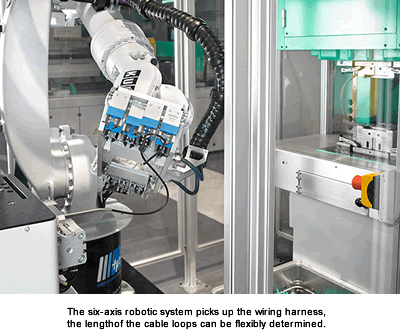
Thanks to the small footprint and high degree of freedom, production units with six-axis robotic systems offer high flexibility and functionality, even in the most restricted spaces, and work well with low hall heights, clean room applications, or link facilities. One such system is a complex production cell for encapsulation of cables, based on a vertical injection molding machine. This application demonstrates the efficiency of a fully automated system: It comprises a vertical injection molding machine, a six-axis robotic system, and a system for supplying the wiring harness.

Using a six-axis robotic system on the vertical machine means no need for manual preparation and insertion of the cables to be encapsulated. Through its nonlinear mobility, a less complex gripper and peripheral device design is feasible and cost-effective. Six-axis robotic systems are ideally suited for all complex handling tasks.
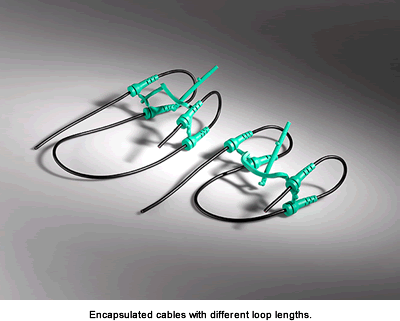
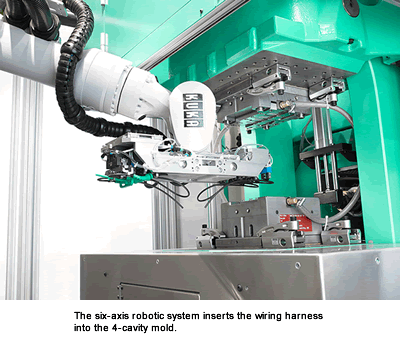
A highlight of this method is the versatile handling of the flexible cables. The wiring harness is inserted automatically into several cavities, at different positions in the four-cavity mold. The length of the cable loops can be flexibly determined.
Programming the Six-Axis Robotic System
A threshold in the use of six-axis robotic systems was crossed with their programming, which was very laborious and feasible only with special programming knowledge. Working in collaboration with the system integrator, Arburg implemented the Selogica user interface in the control system of Kuka robotic systems. This provides decisive benefits for users: After a single brief training session, robotic sequences can be independently programmed. Online communication extends far beyond the Euromap interface and offers functions such as the synchronization of movements and simplified machine start-up. This results in shorter set-up and cycle times.
The higher functionality is apparent in how the robotic system automatically returns to the start position when production is interrupted, making quick restarts easier. Moreover, the separation of random samples, as well as good and rejected parts, is programmable, as are special sequences for start-up and shutdown cycles. This is particularly important when encapsulating inserts and when processing multiple components in order to be able to automatically manufacture completely trouble-free. Interestingly, for complex production tasks, the communication between the robotic system and core pullers is not limited to two, as it is with the Euromap connection.
Complex Process Made Simple with Control System
With its graphic user interface, sequence editor, and real-time plausibility check, the user-oriented Selogica control system provides intuitive machine and peripheral management geared towards the actual sequence. The machine sequences can be programmed by means of a sequence editor with graphic user interface, using symbols. Every function has its own symbol with an associated parameter page. Especially practical is the direct plausibility check during input. This rules out errors from the outset, which is particularly advantageous in the case of complex sequences. Every user change can be approved, logged, and easily traced. By utilizing user ID cards with the associated hierarchically ranked access authorizations, the control systems recognizes who has operated the machine and when.
Moreover, with the Selogica control system, complete production systems, in which upstream and downstream processes are integrated, including the associated peripheral devices and six-axis robotic systems, can be controlled centrally. For quality assurance purposes, all process parameters of the dosage system can be logged via an Ethernet interface. Comprehensive monitoring functions provide process reliability, traceability, and reliable molded part production at the highest quality level.
Extensive Integration Simplifies Operation
The robotic system control unit and the machine control system are coupled together in such a way that following creation of the robotic program, all further actions can be controlled from the injection molding machine via its control panel. Switching the drive on and off, starting and stopping production, pre-selection of operating modes, acknowledgment of alarms, and the management of operating authorizations are possible, for example. The robotic program can also be stored on the Compact Flash card together with the machine program. This means that no separate program management will be required for the robotic system.
Extensive Range of Vertical Machines
The vertical injection molding machines cover a clamping force range from 125 to 4000 kN. They feature a fixed, vertical clamping unit, designed as a free-space system, which operates with a down-stroking movement, preventing the inserts from slipping on the fixed mold half. The machine models are modular in design and enable various combinations in terms of clamping force and injection unit. Because the injection units can be arranged vertically or horizontally, injection can take place either centrally or into the parting line. Thanks to the free-space system and low table heights, these vertical machines are suitable for both manual and automated insertion and removal of molded parts. They can also be optionally equipped with rotary or sliding tables and are therefore also suitable for integration in complete production lines. The versatile configuration options ensure that vertical machines are ideally suited to the production requirements at hand and can also be easily integrated in automated production lines. The automation solutions extend through to complete turnkey systems, which Arburg, as a main contractor, designs, implements, and commissions.[hr]
By Oliver Giesen, Department Manager Projects, ARBURG GmbH + Co KG



