What are Test & Measurement Connectors?
Meet the Connector: Test & Measurement Connectors
As systems become more complex and integrate more functions on a circuit. semiconductor testing has become a particularly significant area for connectors used in Test & Measurement. Test equipment measures the electrical or mechanical properties, performance, and behavior of components or systems. Connectors of all types are subject to test procedures, and the test equipment may itself include connectors. Test procedures can be mechanical, such as insertion/extraction force, retention force, axial and lateral bending, or cable pulling. It may also be electrical and include contact or insulation resistance, current cycling, insertion loss, or shielding effectiveness.
Test & Measurement plays a vital role in various stages of a product lifecycle, from research and development to manufacturing, deployment, and maintenance. It ensures that products meet quality standards, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations. Moreover, it fosters continuous improvement, optimization, and innovation by providing valuable feedback and insights for design and performance enhancements.
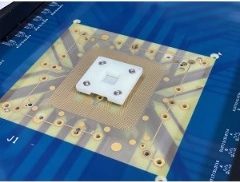
The Galileo is an innovative, low-profile test socket from Smiths Interconnect. It provides outstanding electrical and mechanical performance for IC test customers who need a cost effective, rapid delivery solution.
Connectors Used in Test & Measurement Equipment
Test & Measurement uses a variety of interconnects to establish reliable connections with different devices and components. The specific connectors employed can vary depending on the type of instrument, its intended application, and the required electrical and mechanical characteristics. Commonly used cable and connector types used in Test & Measurement equipment include:
BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman): BNC connectors are widely used in Test & Measurement equipment, especially for applications involving RF (radio frequency) signals. They provide a secure connection and are easy to connect and disconnect.
SMA (SubMiniature version A): SMA connectors are commonly used in high-frequency applications. They offer excellent performance at microwave frequencies and are often employed in RF and microwave test setups.
N-Type: N-Type connectors are larger and provide good performance at higher frequencies. They are frequently used in RF applications, such as antenna connections and high-power measurement equipment.
TNC (Threaded Neill-Concelman): TNC connectors are similar to BNC connectors but have a threaded interface. They provide a more secure connection and are often used in applications requiring higher mechanical stability.
SMB (SubMiniature version B): SMB connectors are compact, push-on connectors used for applications requiring reliable connections at frequencies up to several GHz. They are commonly employed in Test & Measurement equipment, particularly in instrumentation and communications devices.
SMC (SubMiniature version C): SMC connectors are smaller than SMB connectors and provide a higher frequency range, typically up to 10 GHz. They are commonly found in Test & Measurement equipment and other electronic devices.
USB (Universal Serial Bus): USB connectors are extensively used in Test & Measurement equipment for data transfer and device control. They provide a standardized interface for connecting various devices, such as oscilloscopes, data loggers, and multimeters.
Ethernet (RJ-45): Ethernet connectors, often utilizing the RJ-45 interface, are employed for network connectivity in Test & Measurement equipment with networking capabilities. They enable communication and data transfer between instruments and computer networks.
GPIB (General Purpose Interface Bus): GPIB connectors, also known as IEEE 488 connectors, are used in older Test & Measurement equipment to establish connections based on the GPIB standard. They were commonly used for instrument control and data transfer in the past but have been largely replaced by other interfaces.
Test sockets: A test socket is an electromechanical interface that delivers extremely clean electrical signals paths. Test Sockets are used to test high frequency IC’s without soldering them on to a PCB.
Banana plugs and jacks: Banana plugs and jacks are commonly used in low-frequency applications for connecting various types of test leads, such as those used with multimeters and power supplies.
Micro-coaxial cables: Micro-coaxial cables are flexible coaxial cables with a smaller outer diameter than conventional coax-cables (1 mm or less), enabling these cables to take up less space in a test application. These cables typically are paired with micro coax connectors.

TF-047 Micro-Coaxial Cables from Times Microwave Systems are coaxial assemblies constructed to length and with designated input and output connectors.
Test probes: Electrical test probes establish a connection between a circuit under test and the measuring instrument.

binder’s M5, M8, and M12 sensor connectors (M12 shown above) are ideal for industrial Test & Measurement applications such as machine parameter monitoring, thickness gauges, video probes for remote inspection, and soil moisture sensors.
Types of Tests
Common tests conducted in Test & Measurement include:
Electrical Testing: This includes tests to measure electrical parameters such as voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, inductance, and frequency. Instruments like multimeters, oscilloscopes, and signal generators are used for electrical testing.
Signal Analysis: Test & Measurement equipment is utilized to analyze signals and waveforms. This involves tests like spectrum analysis, frequency analysis, distortion analysis, and modulation analysis. Spectrum analyzers, network analyzers, and audio analyzers are commonly used for signal analysis.
Functional Testing: Functional testing verifies the functionality and performance of electronic devices or components. It involves applying stimuli and measuring the corresponding response to ensure proper operation. This can be done using various instruments such as function generators, logic analyzers, and protocol analyzers.
RF and Microwave Testing: RF and microwave testing involve measurements and tests performed at high frequencies. This includes tests such as power measurements, impedance matching, network analysis, and antenna testing. Instruments like RF power meters, vector network analyzers, and spectrum analyzers are used for RF and microwave testing.
Environmental Testing: Test & Measurement equipment is employed to assess the performance and reliability of devices under different environmental conditions. This may involve tests for temperature, humidity, vibration, shock, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Environmental chambers, vibration testers, and EMI receivers are used for environmental testing.
Protocol Testing: Protocol testing involves analyzing and validating the communication protocols used in various devices and systems. It ensures compatibility, reliability, and adherence to standard protocols. Instruments such as protocol analyzers and logic analyzers are used for protocol testing.
Destructive/Non-Destructive Testing: A product, component, or materials is tested to the point of deformity or destruction to analyze its point of failure. Non-destructive testing uses inspection methods that do not damage a material or asset in any way.
Power Quality Analysis: Power quality testing involves evaluating the quality and stability of electrical power systems. It includes tests for voltage fluctuations, harmonics, power factor, and energy consumption. Power analyzers and power quality analyzers are used for power quality analysis.
Safety Testing: Safety testing ensures that electrical devices and equipment meet specified safety standards and regulations. It includes tests for insulation resistance, ground bond, leakage current, and electrical safety. Insulation testers, and safety analyzers are commonly used for safety testing.

Rosenberger offers a variety of products for the Test & Measurement market, including cable assemblies used in RF testing.
Test Processes
The Test & Measurement process typically takes the following steps:
Test Planning: Defining the objectives, requirements, and test parameters based on the specific needs of the product or system being tested.
Test Setup: Configuring the test environment, connecting the appropriate instruments, and preparing the device under test (DUT) for measurement.
Test Execution: Applying controlled conditions, stimuli, or inputs to the DUT and measuring its response. This may involve instruments such as oscilloscopes, multimeters, spectrum analyzers, or network analyzers.
Data Analysis: Processing and analyzing the collected data to gain insights, identify patterns, inconsistences, or failure points, and gain understanding about the performance and characteristics of the DUT.
Reporting and Documentation: Documenting the test results, including measurements, observations, analysis, and issues or recommendations needed for quality control, compliance, and future reference.
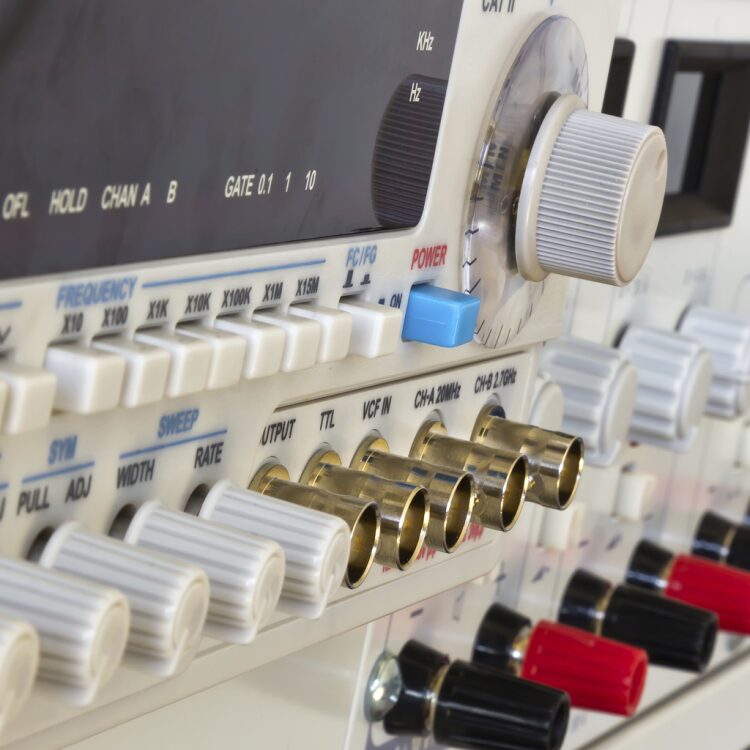

Radiall offers ATE test benches which can automatically perform measurements and quickly evaluate test results. ATE are widely used to test RF sub-systems in avionics, wireless communications and military applications like radars.
Markets, Sectors, and Applications
Automotive, Datacom/Telecom, Test & Measurement, Medical, Military and Aerospace, Consumer, and others
Every industry requires industry-specific testing and uses components that have been subject to testing. Standards bodies and safety and regulatory compliance organizations conduct rigorous tests to ensure products meet their specific safety and performance guidelines. Test & Measurement plays a key role in regulatory, certification, and standards bodies, including UL, CE, DIN, IEC, RoHS, REACH, IEEE, IP, and ISO.

UL conducts extensive testing for safety and performance, including medical device EMC testing and compliance certification.
Suppliers
Amphenol Communications Solutions, binder, BizLink, CarlisleIT, Cinch Connectivity Solutions, EDAC, Fischer Connectors, Lemco, Nicomatic, Smiths Interconnect, Radiall, Rosenberger, RS, Samtec, TE Connectivity, Times Microwave Systems, Ironwood Electronics, LEMO, Pasternack, Stäubli
Like this article? Check out our other Meet the Connector and Networking articles, our Datacom/Telecom Market Page, and our 2023 and 2022 Article Archive.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- Where in the World is Amphenol LTW’s Luc Kan? - April 23, 2024
- TE Connectivity’s Sustainability Efforts Pay Off - April 23, 2024
- What is a VGA Connector? - April 23, 2024





