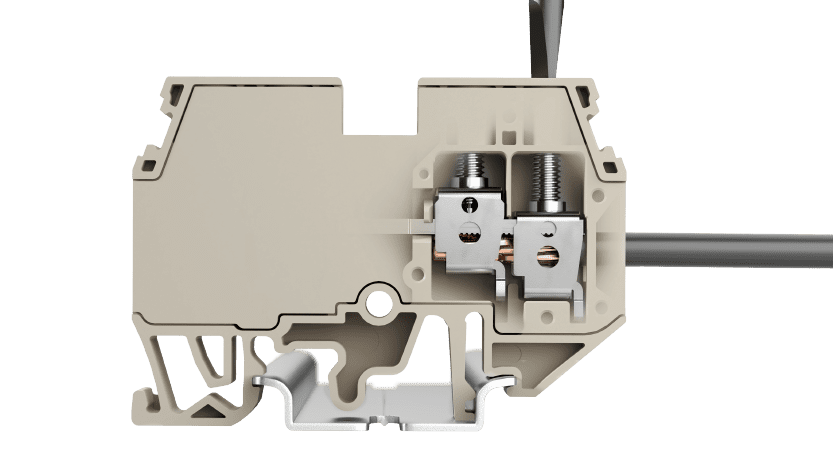
What are DIN Rail Terminal Blocks?
Meet the Connector: DIN Rail Terminal Blocks
DIN rail refers to a mounting system in the form of globally standardized long metal strips used to attach electrical and industrial control products in equipment cabinet racks. The DIN Rail itself is a mechanical component support with no connective or conductive capability. DIN stands for Deutsche Institut für Normung, the German Institute of Standards. This rack-mounting system was developed in Germany in the late 1920s and gained increasing popularity in Europe in the 1950s and soon after found worldwide acceptance.
DIN rail terminal blocks are attachments that protect electrical equipment by preventing short circuits and excess current surges across connecting wires. They are made from plastic or other insulating materials. They provide a safe interface between the components on the DIN rail.
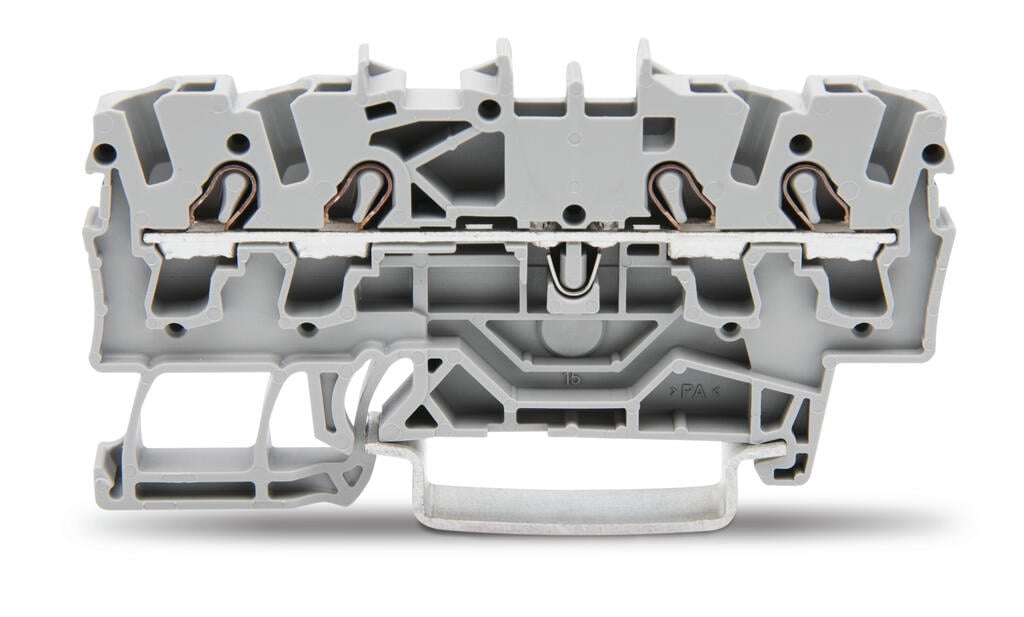
WAGO’s 4-conductor through terminal block features CAGE CLAMP push-in technology.
DIN rail terminal blocks create a complete circuit by allowing the connection of wiring from one piece of equipment to the input-output ports on other equipment. They are widely used in electrical cabinets and industrial racks to protect complex equipment. They are a standard component in telecommunications, building management, energy conservation, HVAC systems, power supplies, lighting control, and vehicle electronics.
Terminal blocks are commonly used in industrial settings. They can be as simple as a single-pole connection (one wire and one circuit). More advanced connectors have two or more levels (parallel single-pole connections) or multiple connections in rows. Terminal block connectors make it easy to repair or replace wiring.
Design Notes
- DIN rail terminal blocks are compact by design, however, when available space is a particular concern, miniature and micro-miniature versions are available.
- Some contain fuses for additional protection in equipment such as sensors and relays, sometimes called DIN rail fuse holder terminal blocks.
- DIN rail terminal blocks come with different current ratings that may be indicated by color coding.
Number of levels:
Single-level model (single wire connection or feed through), dual-level model (one connection above a second connection; the second functions as a second terminal block in essentially the same space as a single-level model). Triple- and quadruple-level models are available, as well as high-end eight- and sixteen-level options.

Examples of rails used in control cabinet construction from Weidmuller. DIN EN 60715 standardized components serve as a universal carrier for electronic equipment.
Termination types:
- Screw terminal blocks secure wiring with a clamp. The inserted screw tightens the clamp and presses the wire into place. Spring-loaded clamps offer a secure, vibration-resistant connection.
- Ring terminal blocks, also called plug-in or push-in terminals, use preinstalled nuts and allow the wires to be pushed into the connection gaps. They are generally four-level models and are smaller than standard DIN rail terminal blocks, saving space.
- Ground terminal blocks (also known as earth terminal blocks) require direct earthing of the wiring. This means it is connected to the ground to discharge any excess electrical charge. They feature green and yellow housing.
Cable Sizes:
The DIN rail terminal block must be fully compatible with the attached cabling. Cable sizes are measured in two ways:
- Diameter – either edge to edge including the insulation or just the inner conducting wire
- Cross-sectional area (CSA), the complete size of the cross-section of the wire, shown in mm2.
Markets include industrial, automotive, and transportation.
Suppliers include Molex, Phoenix Contact, SCHURTER, TE Connectivity, Waytek, WAGO, and Weidmüller

TE Connectivity’s MTC6 thermocouple terminal blocks from Powell Electronics is adapted to many types of thermocouples and requires only 6 mm of space, allowing 50 terminals per foot of rail. Only one part number is needed for all configurations.

Molex DIN-rail or panel-mountable High-Current Universal-Clamp Terminal Blocks, supplied by Avnet, offer a versatile solution for high-current and voltage applications requiring aluminum-to-aluminum, copper-to-copper, or aluminum-to-copper terminations.
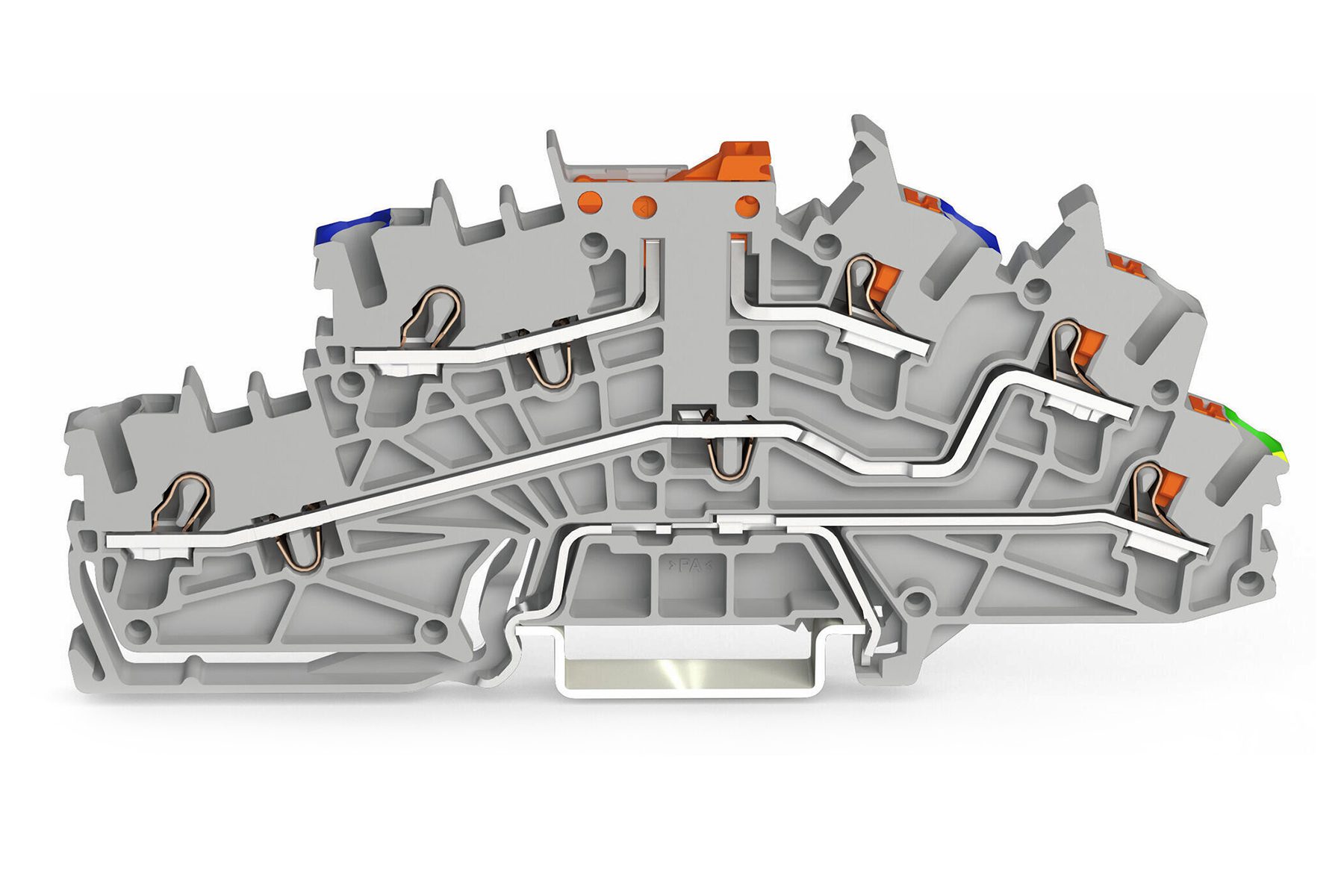
WAGO’s TOPJOB S multi-level installation terminals include push-button and hybrid variants for fusing or blade-style disconnect, as well as direct ground connection to the DIN rail.
Like this article? Check out our other Meet the Connector articles, our Industrial Market Page, and our 2023 and 2022 Article Archive.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.
- Sealing Success: Overmolding for More Secure Connections - April 23, 2024
- Medical Cable Assemblies Product Roundup - April 23, 2024
- Mezzanine Connectors Product Roundup - April 16, 2024