Smart Home Technologies Integrate IoT to Provide Convenience and Cost-Savings
Consumers have quickly adopted convenient and cost-saving Internet of Things (IoT) technologies for home appliances, entertainment devices, and energy and security systems, reshaping the way we live, work, and manage our properties.
Smart homes are answering consumer demands for ease, entertainment, comfort, and sustainability. Powered by computing devices and information technology, smart homes allow for multiple appliances and devices to be automatically and remotely controlled using a mobile or other networked device. In recent years, the global smart home market has dramatically expanded with the availability of a wide range of high technology products for connected homes. In 2021, the global smart home market was $62.7 billion; by 2030, it is projected to reach $537 billion due to a confluence of factors and trends, including:
- Enhanced technologies: Smart homes rely on wireless technologies to effectively operate. The advent of 5G, has boosted the internet to support an increasing number of users and allow for connectivity across a wider range of smart home devices. The result has been the emergence of new and advanced smart home automation systems covering a spectrum of capabilities, from streaming devices and robotic vacuum cleaners to smart safety and surveillance systems. In addition, the integration of AI has enabled devices to offer more advanced capabilities.
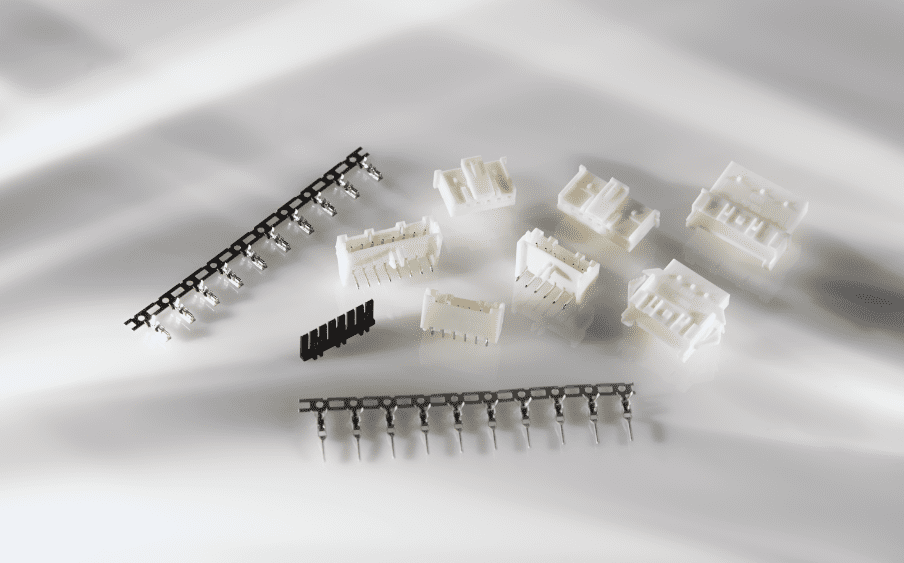
Connected home devices can pack big capabilities into small form factors. TE Connectivity offers Compact Economy Power 2.5 (EP 2.5) connectors for easy assembly of space-limited low-power and signal systems.
- Economic factors and greater ease: Greater disposable income has enabled consumers to spend more on the convenience smart home applications offer. Consumers have started deploying smart and intelligent solutions in everyday tasks to reduce workloads at both home and the workplace. It is expected that the use of smart home devices will have a particular impact on chore automation, cutting an annual average of 100 labor hours for a typical household.
- Energy concerns: Energy efficiency and savings are important aspects of any nation’s economic development. These concerns have become even more critical in the face of rising concerns over global warming. As a result, regulatory bodies in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific are putting forth requirements and incentive programs that call for energy-saving and low carbon emission-oriented solutions. Smart homes heighten control of energy usage and emphasize the use of non-greenhouse gas emitting electrical appliances.
- Surge in smart buildings: One of the great drivers in the growth of smart homes is the actual development of smart buildings. With growing urbanization and the prospect of smart cities becoming more of a reality, a surge in smart buildings will only continue to bolster the market’s overall growth.
Consumer Trends
In addition to technology and market factors, an array of consumer-related trends is also dictating rapid smart home growth.
- Energy savings and sustainability: A desire for energy savings and a growing sense of environmental responsibility top consumer concerns in driving smart home adoption.
- Security and surveillance: Applications include the adoption of video door monitoring, smart alarms, digital locks and lockers, and motion-sensing cameras that can be remotely controlled from a web-enabled device such as a personal computer, tablet, or smart phone.
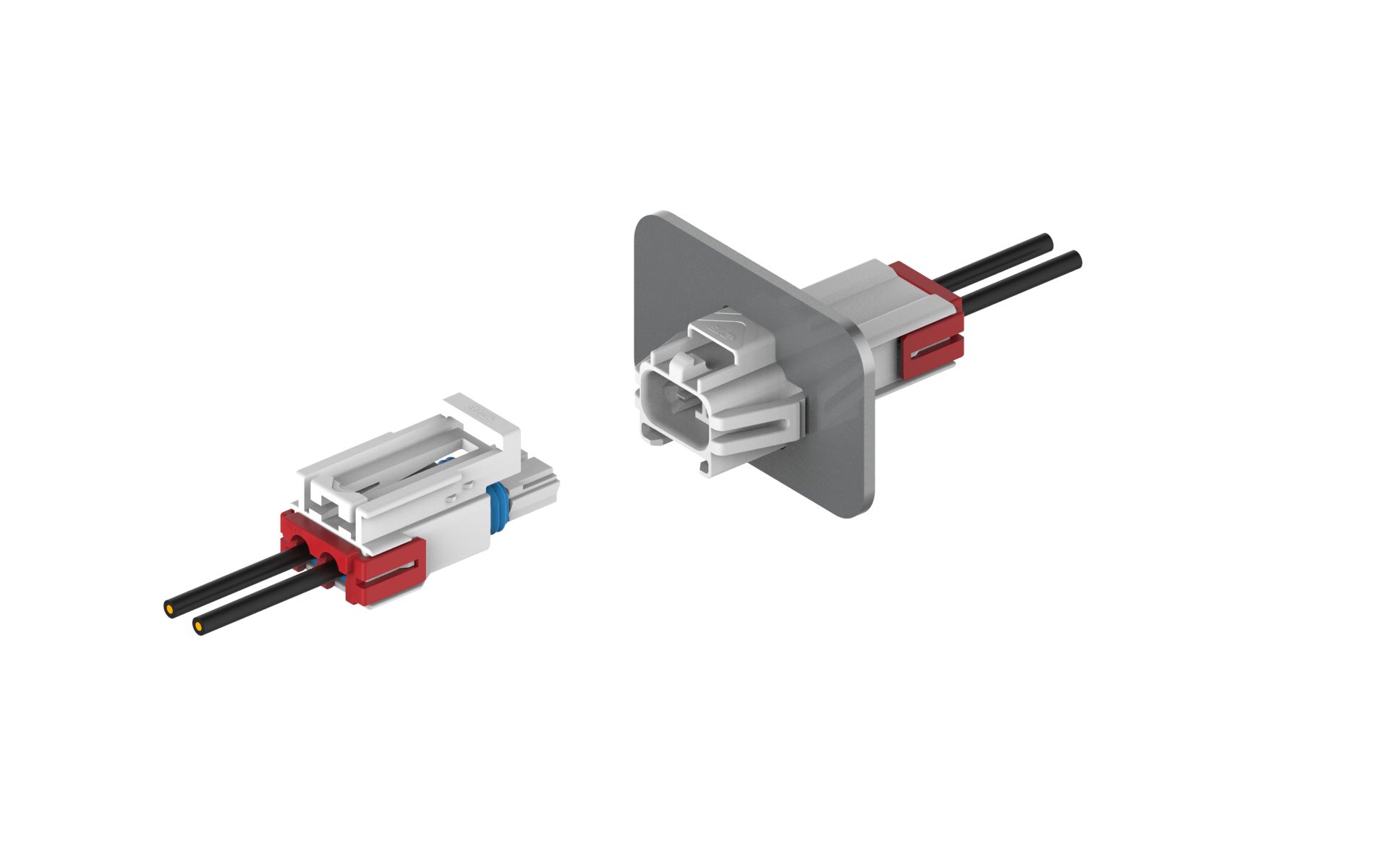
From outdoor security systems to indoor appliances, smart home encompass a range of harsh environments. TE Connectivity’s Power Versa-Lock connectors is a high-performance, wire-to wire power solution featuring perimeter and wire seals that deliver IP67 rated protection.
- Pandemic-related lifestyle changes: Since 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically changed the way people live and work around the world. In turn, these changes have had a direct impact on the growth of smart homes.
- Smart kitchens: Another direct result of the pandemic has been the surge in home cooking. This has directly impacted the growing interest in smart kitchens and in turn, premium-line products with enhanced functionalities.
Challenges
As manufacturers look to support the growth of smart homes, a few challenges will impact consumer acceptance and design issues.
- High installation and maintenance costs: Installing advanced features and integrating technologies, including IoT, AI, machine language, and others, into a fully-equipped smart home, is currently an expense that only a more limited, high-net- worth segment of the consumer landscape can afford.
- Compatibility issues: The smart home market is currently fragmented with many players developing various systems that use a range of technologies. While it is easy to integrate and link up devices from the same manufacturer or vendor, connecting systems from multiple players is a time-consuming job that not only results in a variety of incompatibility issues but more critically, limits functionality, as well as reliability.
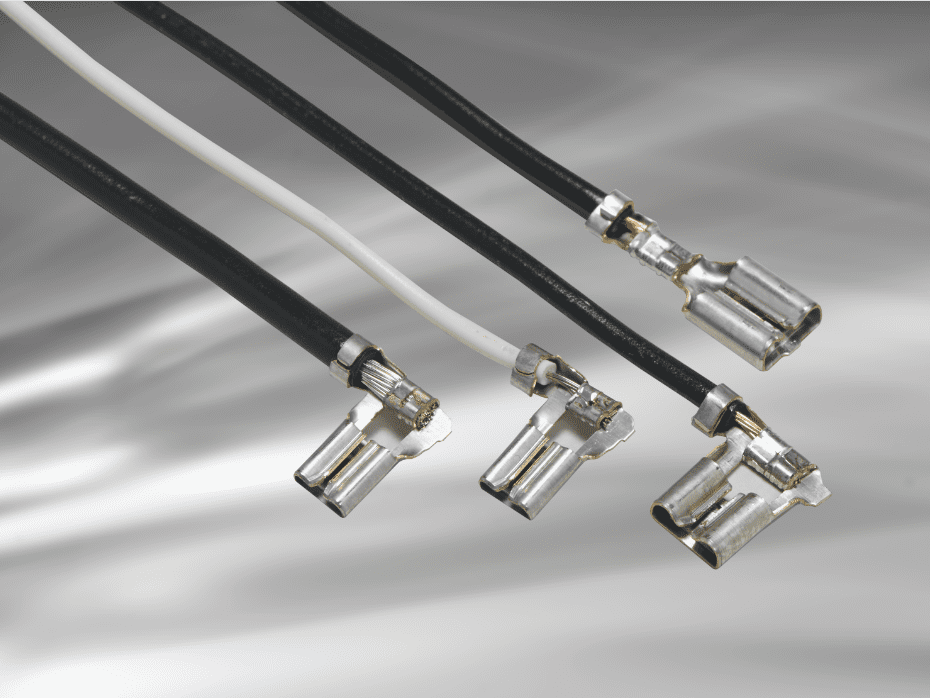

TE Connectivity’s Standard FASTON terminal line offer a robust, quick disconnection, low insertion force (LIF) design with a 2D crimp that allows one terminal and one applicator to cover a full range of wire sizes. This can reduce the number of part numbers to spec in, buy and inventory; reduce applicator cost and set-up; and improve applicator efficiency, making it possible to design and install smart home devices more affordably.
Smart home technologies rely on sensors, connectors, relays, and switch solutions. Innovative sensor solutions. Relays, contactors, and switches can be used nearly anywhere and in any design for access control systems, lighting, building systems, HVAC, and an array of safety-critical applications. From miniature printed circuit board mounted DIP switches to tactile switches for use in household appliances, switches can be used in lighting, building systems, solar, HVAC, and safety applications. Antenna solutions, whether embedded or multi-element external antennas, help create wireless devices and accommodate numerous frequency bands. From standard miniature SMD components to custom products, passive components include resistors, capacitors, chokes, and inductors for use across many applications.
TE Connectivity is sharing insights to help manufacturers capitalize on this opportunity and the various applications that are making smart homes a reality. For deeper analysis of the market factors and consumer trends that are driving growth, as well as the design and technology issues that will impact product development and market adoption, read our latest Smart Home Trend Paper.
Contributed by TE Connectivity
Like this article? Check out our other articles on Smart Homes and Sensors, our Consumer Market Page, and our 2023 and 2022 Article Archive.
Subscribe to our weekly e-newsletters, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook, and check out our eBook archives for more applicable, expert-informed connectivity content.

