Spring Contact Technology for Test & Measurement
Spring Contact Technology for Test & Measurement
The increasing performance requirements of automated test equipment and test fixtures demand more sophisticated contact solutions to meet the needs of contemporary test and measurement challenges.
Advancements in materials, manufacturing technologies, design, and quick prototyping capabilities have led to the emergence of innovative spring contact designs for high-reliability connector assemblies, which provide excellent solutions for temporary connections in OEM and test applications.
Traditional Spring Contact Designs
Traditional spring contacts take the form of simple leaf springs or conventional Pogo pin designs. However, simple leaf spring designs, while offering a low-cost architecture, commonly suffer from early failure due to fatigue and stress.
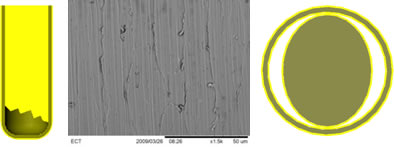
Traditional Pogo pin-style products consume little real estate, are highly versatile for connector design integration, and can deliver a high number of mate/de-mate cycles. However, drawbacks include inefficient management of:
- Critical plunger-to-barrel dimensional and tolerance relationships
- Surface finish challenges of screw-machined parts related to plating adhesion on the outside, as well as the inside of tubular components
- Adverse wear characteristics, including fretting versus mating connectors
- Shock and vibration
Emergence of Advanced Flat Architectures
2D architectures inherently allow relief from the design constraints that have plagued conventional Pogo pin designers for decades. Many methods are used to achieve reliable spring contact architectures, including design concepts such as:
- Radial: Screw machine components and round spring configurations

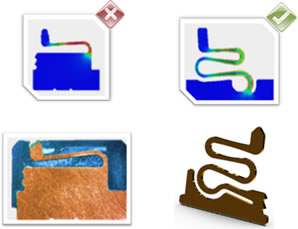
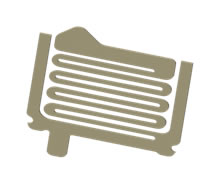
- Flat: Includes spring elements manufactured from flat material stock, ranging from simple leaf spring designs to the innovative and highly reliable designs such as Accordion from ECT
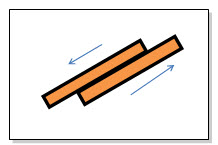
- Flat on Flat: A relatively new approach to enhancing the biasing between contact element components in spring contact assemblies
- Flat Round: A hybrid approach consisting of pairing radial and flat components to create a spring contact element

Advanced manufacturing techniques that facilitate highly desirable flat design features enable tangible functional advantages over traditional contact designs. Those advantages, combined with parallel manufacturing strategies, also improve cost control and quality control benefits over sequential manufacturing strategies.
Flat Characteristics
With flat-on-flat architectures, there is no ID/OD relationship to be concerned with, so there is less interference and greatly improved internal plating quality. Flat-on-flat mating surfaces also allow generous component overlap, providing improved contact resistance and current carrying capacity. Also, flat technologies, which utilize external springs, offer superior compression-to-length ratios over radial designs and spring forces can be reduced to very low levels, which can be critical in dense applications. The extremely smooth exterior of raw, and finished, materials provides efficient operation when in housings and have excellent plating adhesion.
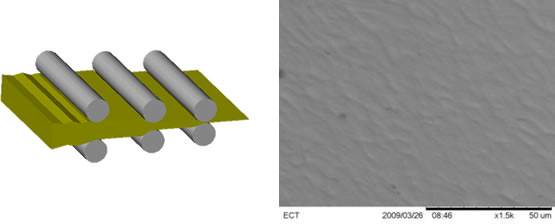
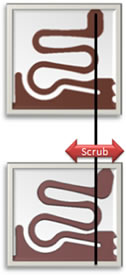 There is also ample opportunity to create hybrid designs to meet various application requirements. Two obvious design combinations include deep draw barrel with flat plunger and radial barrel with flat plunger. Flat components can also be designed to provide enhanced performance at the point of internal contact, such as the addition of wiping features, as shown below. Flat designs allow for deliberate “scrub” capability to be introduced. This removes oxides from contacts and mates and wipes away foreign debris, diminishing the chance of failure due to contamination or plating breakdown.
There is also ample opportunity to create hybrid designs to meet various application requirements. Two obvious design combinations include deep draw barrel with flat plunger and radial barrel with flat plunger. Flat components can also be designed to provide enhanced performance at the point of internal contact, such as the addition of wiping features, as shown below. Flat designs allow for deliberate “scrub” capability to be introduced. This removes oxides from contacts and mates and wipes away foreign debris, diminishing the chance of failure due to contamination or plating breakdown.

Flat components can also be oriented to be in line with or perpendicular to test targets or mating contacts in connector systems. This provides opportunities for improved interoperability, signal integrity, current-carrying capacity, and overall contact integrity.
With both flat and radial component designs available, connectors can be configured for various termination requirements, including thru-hole, surface-mount, blind-mate, and right-angle mate.
Materials
Materials selection for flat components also expands the designer’s ability to meet connector performance requirements. A wide array of copper, phosphorous bronze, steel, and other materials allows flexibility to meet nearly any requirement for hardness or conductivity.
Connector Integration
There are many design-to-specification advantages when utilizing the full array of radial and flat component technologies. They also allow for flexible approaches, such as mating to existing assemblies; custom designs to fit the available dimensional envelope; reduced engineering costs; and designs that incorporate rapid prototyping of high-volume designs.
Advancements in spring contact technology give designers the flexibility to incorporate new concepts that were previously unavailable for test and measurement or OEM applications.
These options offer substantial benefits for the high-reliability connector industry relative to electro-mechanical performance, streamlined manufacturing, and improved supply chain logistics.[hr]
By Brian L. Crisp, Regional Sales Manager, Everett Charles Technologies

